| Korean Med Educ Rev > Volume 24(1); 2022 > Article |
|
Abstract
This study aimed to analyze the subjects, situations, and reflection levels related to role modeling experienced by medical students during their clinical clerkship and their own reflections. This study intends to suggest ways of improving how residents and clinical faculty should treat and teach medical students. Written interviews were conducted regarding senior medical studentsŌĆÖ role modeling experiences during their clinical clerkships in 2018 and 2019. Content analysis was conducted for a total of 224 cases from 196 students. Content analysis revealed three types of role modeling content: subjects (faculty, residents, nurses, peer students), situations (clinical competence, personal qualities, teaching skills), and the level of reflection (critical reflection, reflection, thoughtful action, and habitual action) in each case. As role model subjects, faculty were found to be the paramount role model (n=142, 62.83%). Role modeling was the most frequently performed for clinical competence (n=103, 45.98%). Clinical competence was frequently shown in communication and empathic listening during rounds and outpatient relationships between the patient and doctor. Regarding the level of reflection for role modeling, the number of critical reflections was 86 (38.39%) and that of reflections was 80 (35.71%). In particular, negative role modeling showed a high level of critical reflection in relation to faculty (64.44%) and nurses (8.89%). In conclusion, role modeling of medical students participating in clinical clerkships occurs in situations that the role models are not aware of, with positive or negative effects on the formation of professional identity among medical students.
ņØśĻ│╝ļīĆĒĢÖņāØļōżņØĆ ņØśĻ│╝ļīĆĒĢÖņŚÉ ņ×ģĒĢÖĒĢśļ®┤ņä£ļČĆĒä░ ņóŗņØĆ ņØśņé¼Ļ░Ć ļÉśĻĖ░ ņ£äĒĢ£ ņ¦ĆņŗØ, ņłĀĻĖ░, Ēā£ļÅäļź╝ ņŖĄļōØĒĢśĻ│Ā, ļ│æņøÉņØ┤ļØ╝ļŖö ņ×äņāüĒÖśĻ▓Į ņåŹņŚÉņä£ ļŗżņ¢æĒĢ£ ņ×äņāüĻĄÉņ£Īņ×ÉņÖĆ ĒāĆ ņ¦üņóģņØś ļ│┤Ļ▒┤ņØśļŻīņĀäļ¼Ėņ¦üļōżņØä Ļ┤Ćņ░░ĒĢśļ®┤ņä£ ņĀäļ¼Ėņ¦ü ņĀĢņ▓┤ņä▒ņØä ĒśĢņä▒ĒĢ┤ ļéśĻ░äļŗż. ņ×äņāüņŗżņŖĄ ņżæ ņØśļīĆņāØņØ┤ ļŗżņ¢æĒĢ£ ņ×äņāü ĻĄÉņ£Īņ×ÉļĪ£ļČĆĒä░ ļ│æļÅÖĻ│╝ ņÖĖļלņŚÉņä£ ĒÖśņ×Éļź╝ ļÅīļ│┤ļŖö ļ▓ĢņØä ņ¦üņĀæ ļ│┤Ļ│Ā ļ░░ņÜ░ļŖö ĻĄÉņ£ĪņØĆ ņØśļīĆņāØņØś ņĀäļ¼Ėņ¦ü ņĀĢņ▓┤ņä▒ņØä ņ£äĒĢ£ Ļ░Ćņן ĒÜ©Ļ│╝ņĀüņØĖ ļĪż ļ¬©ļŹĖļ¦ü ĻĄÉņ£Īļ░®ļ▓ĢņØ┤ļŗż[1,2]. ņ×äņāüņŗżņŖĄ ņżæ ņØśļīĆņāØņØ┤ Ļ▓ĮĒŚśĒĢ£ ļĪż ļ¬©ļŹĖļ¦üņØĆ ĒĢÖņŖĄ ļÅÖĻĖ░ Ļ░ĢĒÖöņÖĆ ņĪĖņŚģ Ēøä ņłśļĀ©ņØä ļ░øĻĖ░ ņ£äĒĢ£ ņ¦äļĪ£ņäĀĒāØņŚÉ Ēü░ ņśüĒ¢źņØä ļ»Ėņ╣£ļŗż[3-5]. ļśÉĒĢ£ ņØśļīĆņāØļōżņØĆ ļĪż ļ¬©ļŹĖņØĖ ņ×äņāüĻĄÉņ£Īņ×Éļź╝ Ļ┤Ćņ░░ĒĢśļ®┤ņä£ ĻĘĖļōżņØś Ēā£ļÅä, Ļ░Ćņ╣śĻ┤Ć, Ē¢ēļÅÖņŚÉ ņśüĒ¢źņØä ļ░øĻĖ░ņŚÉ ļĪż ļ¬©ļŹĖļ¦üņØĆ ņĀäļ¼Ėņ¦ü ņĀĢņ▓┤ņä▒ ĒśĢņä▒ņŚÉ ļ¦żņÜ░ ņżæņÜöĒĢ£ ņŚŁĒĢĀņØä ĒĢ£ļŗż[6,7].
ļĪż ļ¬©ļŹĖļ¦üņØĆ ņ×äņāüĒÖśĻ▓Į ņåŹņŚÉņä£ ĻĄÉņłśņ×ÉņÖĆ ĒĢÖņŖĄņ×É, ļŗżņ¢æĒĢ£ ĻĄÉņ£ĪĒĢÖņĀüņØĖ Ļ┤ĆĻ│ä ņåŹņŚÉņä£ ņāüĒśĖņ×æņÜ®ņØä ĒåĄĒĢ┤ ņä▒ņ░░ĒĢśļŖö Ļ│╝ņĀĢņŚÉņä£ ņØ╝ņ¢┤ļé£ļŗż. ļö░ļØ╝ņä£ ļĪż ļ¬©ļŹĖļ¦üņØĆ ņØśĒĢÖĻĄÉņ£ĪņŚÉņä£ ņżæņÜöņä▒ņØ┤ ņ”ØļīĆļÉśĻ│Ā ņ׳ņ£╝ļ®░, ĒŖ╣Ē׳ ņ×äņāü ĻĄÉņ£Īņ×ÉņØś ņóŗņØĆ ļĪż ļ¬©ļŹĖļ¦ü Ļ░ĢĒÖöļŖö ņØśĒĢÖĻĄÉņ£ĪņØś ĒĢäņłśņĀüņØĖ ņÜöņåīĻ░Ć ļÉśņŚłļŗż[8]. ņ×äņāüņŗżņŖĄņŚÉņä£ ĻĄÉņłśņ×ÉļōżņØĆ ĻĘĖļōżņØś ļ¬©ļōĀ ņāüĒśĖņ×æņÜ®Ļ│╝ Ēā£ļÅäĻ░Ć ĒĢÖņāØļōżņŚÉĻ▓ī ņśüĒ¢źņØä ņżĆļŗżļŖö Ļ▓āņØä ņØ┤ĒĢ┤ĒĢśĻ│Ā, ļĪż ļ¬©ļŹĖļ¦üņØś ņżæņÜöņä▒ņØä ņØĖņŗØĒĢ┤ņĢ╝ ĒĢ£ļŗż. ĒĢśņ¦Ćļ¦ī ļīĆļČĆļČäņØś ļĪż ļ¬©ļŹĖļ¦üņØĆ ļĪż ļ¬©ļŹĖņØ┤ ņØĖņ¦ĆĒĢśņ¦Ć ļ¬╗ĒĢśļŖö ļÅÖņĢłņŚÉ ņØ╝ņ¢┤ļéśļ®░, ņØśļīĆņāØļōżļÅä ņä▒ņ░░ ņŚåņØ┤ ļäśĻĖ░ļŖö Ļ▓ĮņÜ░Ļ░Ć ļ¦Äļŗż[8]. ļö░ļØ╝ņä£ ņ×äņāüĻĄÉņ£Īņ×ÉĻ░Ć ĒÜ©Ļ│╝ņĀüņØĖ ļĪż ļ¬©ļŹĖņØ┤ ļÉśĻĖ░ ņ£äĒĢ┤ņä£ļŖö ļĪż ļ¬©ļŹĖļ¦üņØä ņØśņŗØņĀüņ£╝ļĪ£ ņØĖņŗØĒĢśĻ│Ā ļģĖļĀźĒĢĀ ņłś ņ׳ļÅäļĪØ ņĀäĒÖśņŗ£ņ╝£ņŻ╝ļŖö ĻĄÉņłś Ļ░£ļ░£ĒöäļĪ£ĻĘĖļשĻ│╝ ņĪ░ņ¦üļ¼ĖĒÖöĻ░Ć ņżæņÜöĒĢśļŗż[9].
ņ×äņāüņŗżņŖĄ ņżæ ņØśņé¼ņØś ļĪż ļ¬©ļŹĖļ¦üņŚÉ Ļ┤ĆĒĢ£ ļ¼ĖĒŚīņĀü Ļ│Āņ░░ ņŚ░ĻĄ¼ļź╝ ņé┤ĒÄ┤ļ│┤ļ®┤, Ēü¼Ļ▓ī (1) ĻĖŹņĀĢņĀüņØĖ ņØśņé¼ ļĪż ļ¬©ļŹĖņØś Ēā£ļÅä, (2) ĻĖŹņĀĢņĀüņØĖ ņØśņé¼ ļĪż ļ¬©ļŹĖņØś Ļ░£ņØĖņĀü ĒŖ╣ņä▒, (3) ĒĢÖņāØļōżņØś ņ¦äļĪ£ņäĀĒāØņŚÉņä£ ĻĖŹņĀĢņĀüņØĖ ļĪż ļ¬©ļŹĖņØś ņśüĒ¢ź, (4) ĻĖŹņĀĢņĀüņØĖ ļĪż ļ¬©ļŹĖļ¦üņØś Ļ│╝ņĀĢ, (5) ļČĆņĀĢņĀüņØĖ ļĪż ļ¬©ļŹĖļ¦üņØś ņśüĒ¢ź, (6) ļĪż ļ¬©ļŹĖņØä ņäĀĒāØĒĢśļŖöļŹ░ ļ¼ĖĒÖö, ļŗżņ¢æņä▒Ļ│╝ ņä▒ļ│äņØś ņśüĒ¢źņŚÉ ļīĆĒĢ£ ņŚ░ĻĄ¼Ļ░Ć ņ׳ņŚłļŗż[9]. ņØ┤ ņżæ ĻĖŹņĀĢņĀüņØĖ ņØśņé¼ ļĪż ļ¬©ļŹĖļōżņØś Ēā£ļÅäļŖö ņ×äņāüņĀü Ēā£ļÅä, Ļ░Ćļź┤ņ╣śļŖö ĻĖ░ņłĀĻ│╝ Ļ░£ņØĖņĀü ņ×Éņ¦łņŚÉ ļīĆĒĢ£ Ļ▓āņ£╝ļĪ£ ļéśļēĀ ņłś ņ׳ļŗż[10,11]. ņ×äņāüņĀü Ēā£ļÅäļŖö ĒÖśņ×É ņżæņŗ¼ņØś ņĀæĻĘ╝ļ▓ĢĻ│╝ ĒāüņøöĒĢ£ ņ×äņāüņ¦ĆņŗØĻ│╝ ņłĀĻĖ░ļź╝ ļ░öĒāĢņ£╝ļĪ£ ĒĢ£ ņØĖļ│ĖņŻ╝ņØśņĀü Ē¢ēļÅÖņØä ņØśļ»ĖĒĢ£ļŗż[12-14]. ņØĖļ│ĖņŻ╝ņØśņĀü Ē¢ēļÅÖņØĆ Ļ│ĄĻ░É, ņĪ┤ņżæ, ļÅÖņĀĢņŗ¼ņØä ļ│┤ņŚ¼ņŻ╝ļŖö ŌĆśļČĆļō£ļ¤¼ņÜ┤ ĻĖ░ņłĀŌĆÖļĪ£ ļ¼śņé¼ļÉśļŖö Ļ░£ņØĖņĀü Ēā£ļÅäņØ┤ļŗż[15,16]. Ļ░Ćļź┤ņ╣śļŖö ĻĖ░ņłĀņØĆ ĒĢÖņŖĄņ×ÉņÖĆņØś ņ£ĀļīĆĻ┤ĆĻ│äĒśĢņä▒, ĻĖŹņĀĢņĀüņØ┤Ļ│Ā ļÅäņøĆņØ┤ ļÉśļŖö ĻĄÉņ£ĪĒÖśĻ▓Į ņĪ░ņä▒, ĒŖ╣ņĀĢĒĢ£ ĻĄÉņłśļ▓Ģ Ļ░£ļ░£Ļ│╝ ĒĢÖņŖĄņ×ÉņØś ņä▒ņןņŚÉ ņĀäļģÉĒĢśļŖö Ļ▓āņØä ņØśļ»ĖĒĢ£ļŗż[11,17]. ĻĄÉņ£Īņ×ÉļĪ£ņä£ņØś ļĪż ļ¬©ļŹĖĻ│╝ ņ×äņāüĒÖśĻ▓ĮņŚÉņä£ ļ¦ÄņØĆ ĒÖśņ×ÉņÖĆ ņāüĒśĖņ×æņÜ®ņØä ĒĢśļ®┤ņä£ Ļ│ĄļČĆĒĢĀ ļĢī ņØśļīĆņāØļōżņØĆ ļĪż ļ¬©ļŹĖļĪ£ļČĆĒä░ ĻĄ¼ņ▓┤ņĀüņØĖ ņŚŁĒĢĀ ļ¬©ļŹĖļ¦üņØ┤ ņØ╝ņ¢┤ļé£ļŗż[11,17]. Ļ░£ņØĖņĀü ņ×Éņ¦łņØĆ ĒÜ©Ļ│╝ņĀüņØĖ ļīĆņØĖĻ┤ĆĻ│ä ĻĖ░ņłĀ, ĻĖŹņĀĢņĀüņØĖ ņŗ£Ļ░ü, ņ¦äņŗżņä▒, ĒøīļźŁĒĢ£ ļ”¼ļŹöņŗŁ ņŖżĒé¼Ļ│╝ ĒāüņøöĒĢ©ņŚÉ ļīĆĒĢ£ ĒŚīņŗĀ ļō▒ņØä ņØśļ»ĖĒĢ£ļŗż[11].
ņ×äņāüņŗżņŖĄ ņżæ ļĪż ļ¬©ļŹĖļ¦üņØĆ ļ╣äĻ│ĄņŗØņĀüņØ┤Ļ▒░ļéś ņØśļÅäĒĢśņ¦Ć ņĢŖņØä ļĢī ņØ╝ņ¢┤ļéĀ ņłś ņ׳ņ£╝ļ®░, ĒŖ╣Ē׳ ļČĆņĀĢņĀüņØĖ ļĪż ļ¬©ļŹĖļ¦üņØĆ ļ╣äĻ│ĄņŗØņØ┤Ļ│Ā ņ×Āņ×¼ņĀü ĻĄÉņ£ĪĻ│╝ņĀĢņŚÉņä£ Ļ░Ćņן ĒØöĒĢśĻ▓ī ļ░£ņāØĒĢ£ļŗż[18]. Wear ļō▒[19]ņØĆ ņ×äņāüĒÖśĻ▓ĮņŚÉņä£ ņØśļīĆņāØļōżņØĆ ļČĆņĀĢņĀüņØĖ ļĪż ļ¬©ļŹĖļ¦üņØä Ļ▓ĮĒŚśĒĢśļ®┤ņä£ ļĪż ļ¬©ļŹĖņŚÉ ņŗżļ¦ØĒĢśĻ▒░ļéś ļö░ļØ╝ĒĢ┤ņä£ļŖö ņĢł ļÉ£ļŗżļŖö Ļ▓āņØä ņØĖņ¦ĆĒĢ£ļŗżĻ│Ā ĒĢśņśĆļŗż. ņŚ░ĻĄ¼ņ¦äļōżņØĆ ļČĆņĀĢņĀüņØĖ ļĪż ļ¬©ļŹĖļ¦üņŚÉ ļīĆĒĢ┤ņä£ ļ│┤ļŗż Ļ░ĢļĀźĒĢ£ Ļ┤Ćņŗ¼ņØ┤ ĒĢäņÜöĒĢśļ®░, Ļ░£ļ░®ņĀüņØĖ ĒåĀļĪĀĻ│╝ ņ×äņāü ĻĄÉņ£Īņ×Éļź╝ ņ£äĒĢ£ ĻĄÉņłśĻ░£ļ░£ņŚÉ ļ│┤ļŗż ļ¦ÄņØĆ Ļ┤Ćņŗ¼ņØ┤ ĒĢäņÜöĒĢśļŗżĻ│Ā ņŻ╝ņןĒĢśņśĆļŗż[19].
ĻĄÉņ£Īņ×ÉĻ░Ć ĒĢŁņāü ņØ┤ņāüņĀüņØĖ Ē¢ēļÅÖņØä ĒĢśļŖö Ļ▓āņØĆ ņĢäļŗłļ»ĆļĪ£ ĒĢÖņāØļōżņØĆ ņ×äņāüĒśäņןņŚÉņä£ ļČĆņĀĢņĀüņØĖ ļĪż ļ¬©ļŹĖļ¦üņØä Ļ▓ĮĒŚśĒĢśĻĖ░ļÅä ĒĢśņ¦Ćļ¦ī, ņä▒ņ░░ņØĆ ĒĢÖņāØļōżņØś ļČĆņĀĢņĀüņØĖ ļĪż ļ¬©ļŹĖļ¦üņØä ņśłļ░®ĒĢĀ ņłś ņ׳Ļ│Ā, ĻĄÉņ£Īņ×ÉņØś Ē¢ēļÅÖņØä ņä▒ņ░░ĒĢśĻ│Ā ļ╣äĒīÉņĀüņ£╝ļĪ£ ĒÅēĻ░ĆĒĢśļŖö ņŚŁĒĢĀņØä ĒĢśĻĖ░ņŚÉ ņä▒ņ░░ĻĄÉņ£ĪņØ┤ ĒĢäņÜöĒĢśļŗż[9]. ņ×äņāüņŗżņŖĄ ņżæ ņØśļīĆņāØņØś ņĀäļ¼Ėņ¦ü ņĀĢņ▓┤ņä▒ ĒśĢņä▒ņØä ņ£äĒĢ£ ļĪż ļ¬©ļŹĖļ¦üņØś ĒÜ©Ļ│╝ņĀüņØĖ ĻĄÉņ£Īļ░®ļ▓ĢņØĆ ĒĢÖņāØļōżņØś ņä▒ņ░░ļŖźļĀźņØä ņ┤ēņ¦äĒĢśļŖö Ļ▓āņØ┤ļŗż[20]. ņ×äņāüņŗżņŖĄ ņżæ ņ×äņāü ĻĄÉņ£Īņ×ÉņØś ļĪż ļ¬©ļŹĖļ¦üņŚÉ ļīĆĒĢ£ Ēā£ļÅäļŖö Ļ░£ņØĖņ░©Ļ░Ć Ēü¼ĻĖ░ņŚÉ ņØśļīĆņāØņØä ļīĆņāüņ£╝ļĪ£ ĒĢśļŖö ļĪż ļ¬©ļŹĖļ¦üņØä Ļ░£ņäĀĒĢśļŖö ļģĖļĀźņØ┤ ĒĢäņÜöĒĢśļŗż[21]. ļö░ļØ╝ņä£ ĒĢÖņāØļōżņØ┤ ņ×äņāüņŗżņŖĄ ņżæ ļĪż ļ¬©ļŹĖņØä Ļ┤Ćņ░░ĒĢśĻ│Ā, ņāüĒÖ®ņØä ļ╣äĒīÉĒĢśĻ│Ā, ņäĀļ│äņĀüņ£╝ļĪ£ ļ░øņĢäļōżņØ╝ ņłś ņ׳ļÅäļĪØ Ļ░£ņØĖņĀü ļśÉļŖö ņ¦æļŗ©ņĀü ņ░©ņøÉņŚÉņä£ ņä▒ņ░░ņØś ĻĖ░ĒÜīļź╝ Ļ▓ĮĒŚśĒĢśļŖö Ļ▓āņØĆ ņĀäļ¼Ėņ¦ü ņĀĢņ▓┤ņä▒ ĒśĢņä▒ņŚÉ ĒĢäņłśņĀüņØĖ ņÜöņåīņØ┤ļŗż[22-25].
Wald ļō▒[26]ņØĆ ņØśĒĢÖĻĄÉņ£ĪņŚÉņä£ ņä▒ņ░░ņĀü ĻĖĆņō░ĻĖ░ļź╝ ņ£äĒĢ£ ņä▒ņ░░ ĒÅēĻ░ĆņłśņżĆņØä 5ļŗ©Ļ│äļĪ£ Ļ░£ļ░£ĒĢśņśĆļŗż. 1ļŗ©Ļ│äļŖö ņä▒ņ░░ ņŚåņØ┤ ņé¼ņŗżņØä ņä£ņłĀĒĢśļŖö ņłśņżĆņØĖ ļŗ©ņł£ ļ¼śņé¼ņØ┤ļ®░, 2ļŗ©Ļ│äļŖö ņä▒ņ░░ ņŚåņØ┤ ņāüĒÖ®Ļ│╝ ļŖÉļéīņØä ņ×ÉņäĖĒĢśĻ▓ī ņä£ņłĀĒĢśļŖö ņłśņżĆņØĖ ļŗ©ņł£ ļŖÉļéīņØ┤ļ®░, 3ļŗ©Ļ│äļŖö ņé¼Ļ▒┤ņØä ņØ┤ĒĢ┤ĒĢśĻ│Ā ņ¦łļ¼ĖĒĢśĻ│Ā ļČäņäØĒĢśļĀżļŖö ņłśņżĆņØĖ ļŗ©ņł£ ņä▒ņ░░ņØ┤ļ®░, 4ļŗ©Ļ│äļŖö ņ×ÉņŗĀņØś Ļ░Ćņ╣ś, ņŗĀļģÉņØä ļ░öĒāĢņ£╝ļĪ£ Ēśäņ×¼ņÖĆ ļ»ĖļלņŚÉ ļīĆĒĢ£ Ē¢ēļÅÖņØś Ļ▓░Ļ│╝ļź╝ ĒāÉĻĄ¼ĒĢśĻ│Ā ļ╣äĒÅēĒĢśļŖö ņłśņżĆņØĖ ļ╣äĒīÉņĀü ņä▒ņ░░ņØ┤ļŗż. ļ¦łņ¦Ćļ¦ē 5ļŗ©Ļ│äļŖö Ē¢ēļÅÖņØś ļ│ĆĒÖöļź╝ ņØ┤ļüäļŖö ņłśņżĆņØĖ ļ│ĆĒśüņĀü ĒĢÖņŖĄņØ┤ļŗż. ļö░ļØ╝ņä£ ņØśĒĢÖĻĄÉņ£ĪņŚÉņä£ ņä▒ņ░░ĒĢÖņŖĄņØĆ ņØśļīĆņāØļōżņŚÉĻ▓ī ņĀäļ¼Ėņ¦ü ņĀĢņ▓┤ņä▒ ĒśĢņä▒ņØä Ļ░ĢĒÖöĒĢśĻ│Ā, ļ╣äĒīÉņĀü ņé¼Ļ│Āļź╝ ĒĢśļŖö ļŹ░ ļÅäņøĆņØä ņżĆļŗż[27].
ņØśļīĆņāØļōżņØĆ ņĀäļ¼ĖņØś, ņĀäĻ│ĄņØś ļō▒ ņ×äņāü ĻĄÉņ£Īņ×ÉļĪ£ļČĆĒä░ ņØśņé¼ņØś ĒĢäņłśņĀüņØĖ ņŚŁĒĢĀĻ│╝ ĒŖ╣ņ¦ĢņØä ĒīīņĢģĒĢśļ®░, ĻĄÉņ£Īņ×ÉļōżņØś Ē¢ēļÅÖĻ│╝ Ēā£ļÅä ļō▒ņØä Ļ┤Ćņ░░ĒĢśĻ│Ā ņä▒ņ░░ĒĢśļŖö Ļ│╝ņĀĢņŚÉņä£ ņĀäļ¼Ėņ¦ü ņĀĢņ▓┤ņä▒ņØä ĒśĢņä▒ĒĢ┤ ļéśĻ░äļŗż[28]. ņ×äņāü ĻĄÉņ£Īņ×ÉļōżņØś ļĪż ļ¬©ļŹĖļ¦ü ņŚŁļ¤ēņØĆ ņØśļīĆņāØļōżņØś ņĀäļ¼Ėņ¦üņŚģņä▒ Ļ░£ļ░£Ļ│╝ ĻĘĖļōżņØś ņłśĒ¢ēņä▒Ļ│╝ņŚÉļÅä ņśüĒ¢źņØä ļ»Ėņ╣£ļŗżļŖö Ļ▓āņØä ņØĖņŗØĒĢ┤ņĢ╝ ĒĢ£ļŗż[29]. ļ░śļ®┤, ņ×äņāü ĻĄÉņ£Īņ×ÉņŚÉ ļīĆĒĢ£ ļČĆņĀĢņĀüņØĖ ļĪż ļ¬©ļŹĖļ¦üņØĆ ņĀäļ¼Ėņ¦üņŚģņä▒ Ļ░£ļ░£Ļ│╝ņĀĢņŚÉņä£ ĒØöĒ׳ ļ│╝ ņłś ņ׳ļŖö ĒśäņāüņØ┤ļŗż[30]. ļśÉĒĢ£ ļČĆņĀĢņĀüņØĖ ļĪż ļ¬©ļŹĖļ¦üņØĆ ĒāĆ ņ¦üņóģņØś ļ│┤Ļ▒┤ņØśļŻīņØĖĻ│╝ ĒĢÖņāØ Ļ░äņØś ņāüĒśĖņ×æņÜ®ņŚÉņä£ ļéśĒāĆļéĀ ņłś ņ׳ņ£╝ļ»ĆļĪ£[31], ļŗżņ¢æĒĢ£ ņØśļŻī ņĀäļ¼Ėņ¦ü Ļ░äņØś ņŚŁĒĢĀņØä ņØ┤ĒĢ┤ĒĢĀ ņłś ņ׳ļŖö ļĪż ļ¬©ļŹĖļ¦ü ĒøłļĀ©Ļ│╝ Ļ░£ņäĀņØä ņ£äĒĢ£ ļģĖļĀźņØ┤ ĒĢäņÜöĒĢśļŗż[32]. ļö░ļØ╝ņä£ ņ×äņāüĻĄÉņ£Īņ×ÉņÖĆ ĒāĆ ņ¦üņóģĻ░äņØś ļĪż ļ¬©ļŹĖļ¦ü Ļ░ĢĒÖöļź╝ ņ£äĒĢ£ ĻĄÉņłśĻ░£ļ░£ĒöäļĪ£ĻĘĖļש Ļ░£ļ░£ņØ┤ ņżæņÜöĒĢśļ®░, ņØ┤ļŖö ņä▒ņ░░Ļ│╝ Ļ▓ĮĒŚśĒĢÖņŖĄņØä ņ┤ēņ¦äĒĢĀ ņłś ņ׳ļŖö ņåīĻĘĖļŻ╣ ĒśĢĒā£ņØś ņןĻĖ░ ĻĄÉņ£ĪĒöäļĪ£ĻĘĖļשņ£╝ļĪ£ ņ¦äĒ¢ēĒĢĀ ņłś ņ׳ļŗż[33].
ļö░ļØ╝ņä£ ņØ┤ ņŚ░ĻĄ¼ļŖö ņ×äņāüņŗżņŖĄ ņżæ ņØśļīĆņāØļōżņØ┤ Ļ▓¬ņŚłļŹś ņĀäļ¼ĖņØś, ņĀäĻ│ĄņØś, Ļ░äĒśĖņé¼, ļÅÖļŻī ļō▒ ļŗżņ¢æĒĢ£ ļĪż ļ¬©ļŹĖļ¦üņØś Ļ▓ĮĒŚśņØä Passi ļō▒[9]ņØ┤ Ļ│Āņ░░ĒĢ£ ņØśņé¼ņØś ĻĖŹņĀĢņĀü ļĪż ļ¬©ļŹĖ Ēā£ļÅäņØś ņäĖ Ļ░Ćņ¦Ć ņ£ĀĒśĢ(ņ×äņāüņĀü Ēā£ļÅä, Ļ░Ćļź┤ņ╣śļŖö ĻĖ░ņłĀ, Ļ░£ņØĖņĀü ņ×Éņ¦ł)Ļ│╝ ļČĆņĀĢņĀü ļĪż ļ¬©ļŹĖļĪ£ ļČäļźśĒĢśĻ│Ā, ĻĘĖ ļŗ╣ņŗ£ ņØśļīĆņāØļōżņØś ņä▒ņ░░ņØä Wald ļō▒[26]ņØ┤ Ļ░£ļ░£ĒĢ£ ņä▒ņ░░ņłśņżĆ(ļŗ©ņł£ ļ¼śņé¼, ļŖÉļéī ļ¼śņé¼, ļŗ©ņł£ ņä▒ņ░░, ļ╣äĒīÉņĀü ņä▒ņ░░)ņŚÉ ļö░ļØ╝ ļČäņäØĒĢśĻ│Āņ×É ĒĢśņśĆļŗż. ņØ┤ ņŚ░ĻĄ¼ņØś ļ¬®ņĀüņØĆ ņØśļīĆņāØļōżņØś ļĪż ļ¬©ļŹĖļ¦ü Ļ▓ĮĒŚśņØä ļČäņäØĒĢśņŚ¼, ņ×äņāüĻĄÉņ£Īņ×ÉļōżņØ┤ ņØśļīĆņāØļōżņØä ņ¦ĆļÅäĒĢĀ ļĢī ņ¢┤ļ¢ż ļ░®ņŗØņ£╝ļĪ£ ņØśļīĆņāØņØä ļīĆĒĢśĻ│Ā Ļ░Ćļź┤ņ│ÉņĢ╝ ņĀäļ¼Ėņ¦ü ņĀĢņ▓┤ņä▒ ĒśĢņä▒ņŚÉ ņóŗņØĆ ņśüĒ¢źņØä ņżä ņłś ņ׳ņØäņ¦Ć ĻĄÉņłśĻ░£ļ░£ ļ░®ņĢłņØä ņĀ£ņŗ£ĒĢśĻ│Āņ×É ĒĢ£ļŗż.
ņØ┤ ņŚ░ĻĄ¼ļŖö 2018ļģä, 2019ļģäņŚÉ ņŚ░ņäĖļīĆĒĢÖĻĄÉ ņøÉņŻ╝ņØśĻ│╝ļīĆĒĢÖ ņØśĒĢÖĻ│╝ 4ĒĢÖļģäņØä ļīĆņāüņ£╝ļĪ£ ņŗżņŗ£ĒĢśņśĆļŗż. ņØæĻĖēņØśĒĢÖĻ│╝ ĻĄÉņłśņØĖ ņĀĆņ×ÉĻ░Ć ĒĢÖņāØļōżņØś ņØæĻĖēņØśĒĢÖĻ│╝ ņŗżņŖĄĻĖ░Ļ░äņŚÉ ņĀäļ¼Ėņ¦ü ņĀĢņ▓┤ņä▒ ĒśĢņä▒Ļ│╝ņĀĢĻ│╝ ļĪż ļ¬©ļŹĖļ¦üņØś Ļ░£ļģÉņØä ņäżļ¬ģĒĢ£ ļÆż, ņ×äņāüņŗżņŖĄ ņżæ ņ×ÉņŗĀņØ┤ Ļ▓¬ņŚłļŹś ļĪż ļ¬©ļŹĖļ¦üņØś Ļ▓ĮĒŚśĻ│╝ ļŗ╣ņŗ£ ņ×ÉņŗĀņØ┤ ņä▒ņ░░ĒĢ£ ļé┤ņÜ®ņŚÉ ļīĆĒĢ┤ Ļ░äļŗ©ĒĢ£ ņä▒ņ░░ļ│┤Ļ│Āņä£ļź╝ ņ×æņä▒ĒĢśļÅäļĪØ ĒĢśņśĆļŗż. ļé┤ņÜ®ņØĆ ņØæĻĖēņØśĒĢÖĻ│╝ņŚÉ ĻĄŁĒĢ£ĒĢśņ¦Ć ņĢŖĻ│Ā ņĀäņ▓┤ ņ×äņāüņŗżņŖĄĻĖ░Ļ░äņŚÉ Ļ▒Ėņ│É Ļ▓ĮĒŚśĒĢ£ ļé┤ņÜ®ņØä ņĀüļÅäļĪØ ĒĢśņśĆĻ│Ā, ļæÉ Ļ░Ćņ¦Ć ņØ┤ņāüņØś Ļ▓ĮĒŚśņØä ņĀüņ¢┤ļÅä ļÉśļŖö Ļ▓āņ£╝ļĪ£ ņäżļ¬ģĒĢśņśĆļŗż. ņä▒ņ░░ļ│┤Ļ│Āņä£ ļé┤ņÜ®ņØ┤ ļĪż ļ¬©ļŹĖņØ┤ ņŚåĻ▒░ļéś ļĪż ļ¬©ļŹĖļ¦ü ņāüĒÖ®ņØ┤ ņĢäļŗī ļé┤ņÜ® ļō▒ ļČäņäØĒĢśĻĖ░ņŚÉ ļČĆņŗżĒĢ£ Ļ▓ĮņÜ░ļŖö ļīĆņāüņ×ÉņŚÉņä£ ņĀ£ņÖĖļÉśņŚłņ£╝ļ®░, 2ļģä ļÅÖņĢł ņ┤Ø 196ļ¬ģņØä ļīĆņāüņ£╝ļĪ£ 224Ļ▒┤ņØś ļĪż ļ¬©ļŹĖļ¦ü ņé¼ļĪĆļź╝ ņłśņ¦æĒĢśņśĆļŗż. ņØ┤ ņŚ░ĻĄ¼ļŖö ņ▒ģņ×äņŚ░ĻĄ¼ņ×ÉĻ░Ć ņåŹĒĢ┤ ņ׳ļŖö ĻĖ░Ļ┤ĆņØś ņŚ░ĻĄ¼ņŗ¼ņØśņ£äņøÉĒÜīņØś ņŖ╣ņØĖņØä ļ░øĻ│Ā ņ¦äĒ¢ēĒĢśņśĆļŗż(ņŖ╣ņØĖļ▓łĒśĖ: CR321052). ņŚ░ĻĄ¼ņŗ¼ņØśņŚÉņä£ ļÅÖņØśņä£ ņĀ£ņČ£ņØĆ ņāØļץĒĢśĻĖ░ļĪ£ ĒĢśņśĆļŗż.
ņłśņ¦æļÉ£ ņä▒ņ░░ļ│┤Ļ│Āņä£ ņ×ÉļŻīļŖö ļ¬©ļæÉ ņŚæņģĆ ĒīīņØ╝(IBM Corp., Armonk, NY, USA)ļĪ£ ņĀĢļ”¼ĒĢśņŚ¼ ļČäņäØĒĢśņśĆļŗż. ņ×æņä▒ĒĢ£ ļé┤ņÜ®ņØä ņ×äņāüņŗżņŖĄ ņżæ Ļ▓ĮĒŚśĒĢ£ ļĪż ļ¬©ļŹĖ, ļĪż ļ¬©ļŹĖļ¦üņØś ņŻ╝ņĀ£ņÖĆ ļé┤ņÜ®, ņä▒ņ░░ņłśņżĆņ£╝ļĪ£ ļČäļźśĒĢśņśĆļŗż. ļĪż ļ¬©ļŹĖņØĆ ņĀäļ¼ĖņØś(ņ×äņāüĻ░Ģņé¼ ņØ┤ņāü), ņĀäĻ│ĄņØś(ņØĖĒä┤ ĒżĒĢ©), Ļ░äĒśĖņé¼, ļÅÖļŻī, ĻĖ░ĒāĆļĪ£ ļČäļźśĒĢśņśĆļŗż. ļĪż ļ¬©ļŹĖļ¦ü ņŻ╝ņĀ£ļŖö Passi ļō▒[9]ņØ┤ ļČäļźśĒĢ£ ņŻ╝ņĀ£ļź╝ ļ░öĒāĢņ£╝ļĪ£ ņØśņé¼ņØś ĻĖŹņĀĢņĀü ļĪż ļ¬©ļŹĖļ¦ü Ēā£ļÅä ņżæ ņ×äņāüņĀü Ēā£ļÅä, Ļ░Ćļź┤ņ╣śļŖö ĻĖ░ņłĀ, Ļ░£ņØĖņĀü ņ×Éņ¦łĻ│╝ ļČĆņĀĢņĀü ļĪż ļ¬©ļŹĖļ¦üņ£╝ļĪ£ ļČäļźśĒĢśņśĆļŗż. ļĪż ļ¬©ļŹĖļ¦üņØś ļé┤ņÜ®ņØĆ ņ¢┤ļ¢ż ņāüĒÖ®ņŚÉņä£ ļĪż ļ¬©ļŹĖņØś ņ¢┤ļ¢ż Ē¢ēļÅÖņØĖņ¦Ć ļČäņäØĒĢśņśĆļŗż. ņä▒ņ░░ņłśņżĆņØĆ Wald ļō▒[26]ņØ┤ Ļ░£ļ░£ĒĢ£ ņØśĒĢÖĻĄÉņ£ĪņŚÉņä£ ņä▒ņ░░ņĀü ĻĖĆņō░ĻĖ░ļź╝ ņ£äĒĢ£ ŌĆśreflection rubricŌĆÖ ņä▒ņ░░ņłśņżĆņØĖ ļŗ©ņł£ ļ¼śņé¼, ļŖÉļéī ļ¼śņé¼, ļŗ©ņł£ ņä▒ņ░░, ļ╣äĒīÉņĀü ņä▒ņ░░ļĪ£ ļČäļźśĒĢśņśĆļŗż.
ļé┤ņÜ®ļČäņäØņØĆ ņ¦Ćņŗ£ņĀü ļé┤ņÜ®ļČäņäØ(directed content analysis)Ļ│╝ ņĀäĒåĄņĀüņØĖ ļé┤ņÜ®ļČäņäØ(conventional content analysis) ĻĘĖļ”¼Ļ│Ā ļČĆĻ░ĆņĀü ļé┤ņÜ®ļČäņäØ(summative content analysis)ņØä Ļ░ÖņØ┤ ņé¼ņÜ®ĒĢśņśĆļŗż[34]. ņ¦Ćņŗ£ņĀü ļé┤ņÜ®ļČäņäØņØĆ ĻĖ░ņĪ┤ņØś ņØ┤ļĪĀņØ┤ļéś ņŚ░ĻĄ¼Ļ▓░Ļ│╝ļź╝ ļ░öĒāĢņ£╝ļĪ£ ņŚ░ĻĄ¼ņ×ÉļŻīļź╝ ļČäņäØĒĢśļŖö ļ░®ļ▓ĢņØ┤ļ®░, ņĀäĒåĄņĀüņØĖ ļé┤ņÜ®ļČäņäØņØĆ ļé┤ņÜ® ņ×Éņ▓┤ļź╝ ņäĀņ×ģĻ▓¼ ņŚåņØ┤ ņØ┤ĒĢ┤ĒĢśĻ│Ā ļČäņäØĒĢśļŖö ļ░®ļ▓ĢņØ┤ļŗż. ļČĆĻ░ĆņĀü ļé┤ņÜ®ļČäņäØņØĆ ļé┤ņÜ®ņŚÉņä£ ĒŖ╣ņĀĢ ļŗ©ņ¢┤(certain word) ļśÉļŖö ĒŖ╣ņĀĢ ļé┤ņÜ®(content)ņØä ĒÖĢņØĖĒĢśĻ│Ā, ņĀĢļ¤ēĒÖö(quantifying)ĒĢśļŖö ļ░®ļ▓ĢņØ┤ļŗż[34].
ļé┤ņÜ®ļČäņäØ ņĀłņ░©ļź╝ ņłśĒ¢ēĒĢśĻĖ░ ņ£äĒĢ┤ ņ¦łņĀü ņŚ░ĻĄ¼Ļ▓ĮĒŚśņØ┤ ļ¦ÄņØĆ ņŚ░ĻĄ¼ņ×É 2ņØĖņØ┤ Ļ░üĻ░ü ņ×ÉļŻīņŚÉ ļ¬░ņ×ģĒĢśņŚ¼ ĒĢäņé¼ļÉ£ ņ×ÉļŻīļź╝ ļ░śļ│ĄņĀüņ£╝ļĪ£ ņØĮņ£╝ļ®┤ņä£ ņ×ÉļŻīņØś ņĀäņ▓┤ņĀüņØĖ ņØśļ»Ėļź╝ ĒīīņĢģĒĢśņśĆņ£╝ļ®░, ņØśļīĆņāØļōżņØ┤ ņ×äņāüņŗżņŖĄ ņżæ ļĪż ļ¬©ļŹĖļ¦üņØ┤ ņØ╝ņ¢┤ļéśļŖö ļīĆņāüĻ│╝ ņŻ╝ņĀ£, ņä▒ņ░░ņłśņżĆ ļō▒ņØä ĻĄ¼ļČäĒĢśņśĆļŗż. ļæÉ ļ¬ģņØś ļČäņäØņ×ÉĻ░Ć ņ×ÉļŻīņØś ļé┤ņÜ® ņżæ ļĪż ļ¬©ļŹĖļ¦ü ņŻ╝ņĀ£ņÖĆ ņä▒ņ░░ņłśņżĆĻ│╝ Ļ┤ĆļĀ©ĒĢśņŚ¼ ĒĢĄņŗ¼ņĀüņØĖ ņāØĻ░üņØ┤ļéś Ļ░£ļģÉņØä ļéśĒāĆļé┤ļŖö ļŗ©ņ¢┤ņÖĆ ļ¼ĖņןļōżņØä ņČöņČ£ĒĢśĻ│Ā, ļ╣äņŖĘĒĢ£ ņØśļ»ĖņÖĆ ņŻ╝ņĀ£ļź╝ Ļ░Ćņ¦ä ļ¼Ėņןļōżļü╝ļ”¼ ļ¬©ņĢä ņŻ╝ņĀ£ļōżņØä ļÅäņČ£ĒĢśņśĆļŗż. ļŗżņØīņ£╝ļĪ£ļŖö ņŻ╝ņĀ£ļōż Ļ░äņØś ņŚ░Ļ│äņä▒ņŚÉ ĻĘ╝Ļ▒░ĒĢśņŚ¼ ļ│┤ļŗż ņČöņāüņĀüņØ┤Ļ│Ā ĒĢ©ņČĢņä▒ņØ┤ Ēü░ ņŻ╝ņĀ£ļĪ£ ļ¼ČļŖö Ļ│╝ņĀĢņØä Ļ▒░ņ│żļŗż. ļČäņäØĻ│╝ņĀĢņŚÉņä£ ļ▓öņŻ╝ļéś Ļ░£ļģÉņØś ņ░©ņØ┤Ļ░Ć ņ׳ļŖö ļČĆļČäņŚÉ ļīĆĒĢśņŚ¼ ļæÉ ļ¬ģņØś ņŚ░ĻĄ¼ņ×É Ļ░äņŚÉ ņ¦ĆņåŹņĀüņØĖ ļģ╝ņØśņÖĆ ĒśæņØśļź╝ ĒåĄĒĢ┤ ņĪ░ņĀĢĒĢ©ņ£╝ļĪ£ņŹ© Ļ▓░Ļ│╝ņØś ņŗĀļó░ļÅäņÖĆ ĒāĆļŗ╣ļÅäļź╝ ļåÆņØ┤Ļ│Āņ×É ĒĢśņśĆļŗż. ļ¦łņ¦Ćļ¦ēņ£╝ļĪ£ ļĪż ļ¬©ļŹĖ, ļĪż ļ¬©ļŹĖļ¦ü ņŻ╝ņĀ£, ņä▒ņ░░ņłśņżĆ Ļ▓░Ļ│╝ļź╝ ļ╣łļÅäņłśņÖĆ ļ╣äņ£©ļĪ£ Ēæ£ņŗ£ĒĢśĻ│Ā, Ļ░ü ņŻ╝ņĀ£ņŚÉ ļīĆĒĢ£ ļīĆĒæ£ņĀüņØĖ ņśłņŗ£ļź╝ ļÅäņČ£ĒĢśņśĆļŗż.
ņ×äņāüņŗżņŖĄ ņżæ ņØśļīĆņāØņØ┤ Ļ▓ĮĒŚśĒĢ£ ļĪż ļ¬©ļŹĖļ¦ü Ļ▓ĮĒŚśĻ│╝ ņä▒ņ░░ņłśņżĆņØä ļČäņäØĒĢśĻĖ░ ņ£äĒĢ┤ 2018ļģäĻ│╝ 2019ļģä ņØśĻ│╝ļīĆĒĢÖ 4ĒĢÖļģä 196ļ¬ģņ£╝ļĪ£ļČĆĒä░ ņłśņ¦æļÉ£ 224Ļ▒┤ņØś ļĪż ļ¬©ļŹĖļ¦ü Ļ▓ĮĒŚśĻ│╝ ņä▒ņ░░ņłśņżĆņØä ļé┤ņÜ®ņØä ļČäņäØĒĢśņśĆļŗż(Table 1). ļĪż ļ¬©ļŹĖļ¦ü ņŻ╝ņĀ£ļź╝ ņäĀĒ¢ēņŚ░ĻĄ¼ņŚÉņä£ ņĀ£ņŗ£ĒĢ£ ĻĖŹņĀĢņĀü ļĪż ļ¬©ļŹĖļ¦ü ņżæ ņ×äņāüņĀü Ēā£ļÅä, Ļ░Ćļź┤ņ╣śļŖö ĻĖ░ņłĀ, Ļ░£ņØĖņĀü ņ×Éņ¦ł, ļČĆņĀĢņĀü ļĪż ļ¬©ļŹĖļ¦üņ£╝ļĪ£ ļČäļźśĒĢ£ Ļ▓░Ļ│╝, ĻĖŹņĀĢņĀü ļĪż ļ¬©ļŹĖļ¦ü ņżæ ņ×äņāüņĀü Ēā£ļÅäĻ░Ć Ļ░Ćņן ļ¦ÄņĢśņ£╝ļ®░(103Ļ▒┤, 45.98%), ĻĘĖ ļŗżņØīņ£╝ļĪ£ ļĪż ļ¬©ļŹĖņØś Ļ░£ņØĖņĀü ņ×Éņ¦ł(53Ļ▒┤, 23.66%)Ļ│╝ Ļ░Ćļź┤ņ╣śļŖö ĻĖ░ņłĀ(22Ļ▒┤, 9.82%)ļĪ£ ļéśĒāĆļé¼ļŗż. ļČĆņĀĢņĀü ļĪż ļ¬©ļŹĖļ¦üņØĆ 46Ļ▒┤(20.54%) ņ׳ņŚłļŗż. ļĪż ļ¬©ļŹĖ ļīĆņāüņØä ņé┤ĒÄ┤ļ│┤ļ®┤, 224Ļ▒┤ņØś ļĪż ļ¬©ļŹĖļ¦ü Ļ▓ĮĒŚś ņżæ 1Ļ▒┤ņŚÉņä£ ņäĖ ļ¬ģņØś ļĪż ļ¬©ļŹĖņØä ļÅÖņŗ£ņŚÉ ņ¢ĖĻĖēĒĢśņŚ¼, ļĪż ļ¬©ļŹĖņØś ļīĆņāüņØĆ ņ┤Ø 226Ļ▒┤ņØ┤ņŚłļŗż. ļĪż ļ¬©ļŹĖņØĆ ņĀäļ¼ĖņØśĻ░Ć Ļ░Ćņן ļ¦ÄņĢśņ£╝ļ®░(142Ļ▒┤, 62.83%), ņĀäĻ│ĄņØś(60Ļ▒┤, 26.55%), ļÅÖļŻī(15Ļ▒┤, 6.64%), Ļ░äĒśĖņé¼(6Ļ▒┤, 2.65%) ņł£ņ£╝ļĪ£ ļéśĒāĆļé¼ļŗż. ņä▒ņ░░ņłśņżĆņØĆ ļŗ©ņł£ ļ¼śņé¼, ļŖÉļéī ļ¼śņé¼, ļŗ©ņł£ ņä▒ņ░░, ļ╣äĒīÉņĀü ņä▒ņ░░ļĪ£ ļČäļźśĒĢ£ Ļ▓░Ļ│╝, ļ╣äĒīÉņĀü ņä▒ņ░░(86Ļ▒┤, 38.39%)Ļ│╝ ļŗ©ņł£ ņä▒ņ░░(80Ļ▒┤, 35.71%)ņØ┤ ļ¦ÄņĢśļŗż(Table 1).
ņ×äņāüņĀü Ēā£ļÅäņŚÉņä£ļŖö ņĀäļ¼ĖņØśļź╝ ļīĆņāüņ£╝ļĪ£ ĒĢ£ ļĪż ļ¬©ļŹĖļ¦üņØ┤ Ļ░Ćņן ļ¦ÄņĢśņ£╝ļ®░(60Ļ▒┤, 58.25%), ĻĘĖ ļŗżņØīņØĆ ņĀäĻ│ĄņØśņśĆļŗż(38Ļ▒┤, 36.89%). ĒŖ╣Ē׳ ĒÜīņ¦äĻ│╝ ņÖĖļל ņŗ£ ņØśņé¼ņÖĆ ĒÖśņ×ÉņÖĆņØś ņāüĒśĖņ×æņÜ® ņżæ ĒÖśņ×É ņżæņŗ¼ņØś ņåīĒåĄĻ│╝ Ļ│ĄĻ░ÉņĀü Ļ▓ĮĒŚś ĻĘĖļ”¼Ļ│Ā ņ╣£ņĀłĒĢ£ Ēā£ļÅä ļō▒ņŚÉņä£ ņØśļīĆņāØļōżņØĆ ļåÆņØĆ ņä▒ņ░░ņłśņżĆņØś ļĪż ļ¬©ļŹĖļ¦üņØ┤ ņØ╝ņ¢┤ļé¼ļŗż. ņĢäņÜĖļ¤¼ ņ¢┤ļĀżņÜ┤ ņāüĒÖ®ņŚÉņä£ ĒÖśņ×Éļź╝ ļīĆĒĢśļŖö Ēā£ļÅä, ņłśņłĀ ņŗ£ ņØśņé¼ņØś ņ╣©ņ░®ĒĢ©Ļ│╝ ĒÅēņĀĢņŗ¼ņØä ļ│┤ņŚ¼ņżä ļĢī, ņłśņłĀņØä ņ¦äĒ¢ēĒĢĀ ļĢī ļō▒ņØ┤ ņ׳ņŚłļŗż. ņĀäĻ│ĄņØśļź╝ ļīĆņāüņ£╝ļĪ£ ĒĢśļŖö Ļ▓ĮņÜ░ņŚÉļÅä ļĪż ļ¬©ļŹĖļ¦üņØś ņāüĒÖ®ņØĆ ļ╣äņŖĘĒĢśņśĆļŗż(Table 2).
ļĪż ļ¬©ļŹĖņØś ņ×äņāüņĀü Ēā£ļÅäņŚÉ ļīĆĒĢ£ ņä▒ņ░░ņłśņżĆņØä ļČäņäØĒĢ£ Ļ▓░Ļ│╝, ņØśļīĆņāØļōżņØĆ ļ╣äĒīÉņĀü ņä▒ņ░░(36Ļ▒┤, 35.29%)Ļ│╝ ļŗ©ņł£ ņä▒ņ░░(38Ļ▒┤, 37.25%)ņØä Ļ░Ćņן ļ¦ÄņØ┤ ĒĢśņśĆļŗż(Figure 1). ņØśļīĆņāØļōżņØ┤ ļŖÉļéĆ ļĪż ļ¬©ļŹĖņØś ņ×äņāüņĀü Ēā£ļÅäņŚÉņä£ņØś ņä▒ņ░░ņłśņżĆņŚÉ ļö░ļźĖ ņśłņŗ£ļŖö ļŗżņØīĻ│╝ Ļ░Öļŗż. ļīĆļČĆļČä ņØśļīĆņāØļōżņØĆ ļ╣äĒīÉņĀü ņä▒ņ░░Ļ│╝ ļŗ©ņł£ ņä▒ņ░░ņØä ĒåĄĒĢ┤ ĒÖśņ×É-ņØśņé¼ņØś ņāüĒśĖņ×æņÜ® ņåŹņŚÉņä£ ņØśņé¼ņØś ņ╣£ņĀłĒĢ©Ļ│╝ Ļ│ĄĻ░ÉņĀü Ļ▓Įņ▓Ł, ļ░░ļĀż, ĒÖśņ×É ņżæņŗ¼ņØś ņåīĒåĄ ļō▒ņØä Ļ┤Ćņ░░ĒĢśļ®┤ņä£ ņØśņé¼ņŚÉĻ▓ī ĒĢäņÜöĒĢ£ Ļ│ĄĒåĄ ņŚŁļ¤ēņØś ņżæņÜöņä▒ņØä ņØĖņŗØĒĢśņśĆņ£╝ļ®░, ļ»ĖļלņØś ņ×ÉņŗĀņØś Ē¢ēļÅÖņŚÉ ļīĆĒĢ£ Ļ░Ćņ╣śĻ┤ĆņØä ĒśĢņä▒ĒĢśĻ│Ā Ē¢ēļÅÖņØś ļ│ĆĒÖöļź╝ ļŗżņ¦ÉĒĢśņśĆļŗż.
ŌĆ£ņśżĒøä ĒÜīņ¦ä ļĢī, ĒÖśņ×ÉĻ░Ć 40ļ¬ģņØ┤ ļäśļŖö ļéĀņØ┤ ņ׳ņŚłļŗż. ĻĄÉņłśļŗśĻ╗śņä£ ĒÖśņ×É ĒĢ£ ļ¬ģ ĒĢ£ ļ¬ģ ļ│ĖņØĖņØ┤ ļŗżņŗ£ ņŗĀņ▓┤ ņ¦äņ░░ņØä ĒĢśĻ│Ā ĒÖśņ×Éļź╝ ņĢłņŗ¼ņŗ£ĒéżļŖö ļ¬©ņŖĄņØä ļ│┤Ļ│Ā Ļ╣ŖņØĆ Ļ░Éļ¬ģņØä ļ░øņĢśļŗż. ĒÖśņ×Éļź╝ ļé┤Ļ░Ć ļ│┤ļŖö Ļ▓āņØĆ 30ļ¬ģ, 40ļ¬ģņØ╝ņ¦Ć ļ¬©ļź┤ņ¦Ćļ¦ī, ĒÖśņ×ÉļŖö 1ļ¬ģņØś ņØśņé¼ļ¦īņØä ĻĖ░ļŗżļ”¼Ļ│Ā ņ׳ĻĖ░ ļĢīļ¼ĖņŚÉ ĒĢ£ ļ¬ģ ĒĢ£ ļ¬ģ ņĀĢņä▒ņØä ļŗżĒĢ┤ņä£ ĒÖśņ×Éļź╝ ļ┤ÉņĢ╝Ļ▓ĀļŗżĻ│Ā ļŗżņ¦ÉĒĢśĻ▓ī ļÉśņŚłļŗż(critical reflection)ŌĆØ
ŌĆ£ņśżņĀä ĒÜīņ¦äņŚÉņä£ ĒÖśņ×ÉļČäļōżņØä ļ¦īļéśņä£ Ēśäņ×¼ ņāüĒÖ®Ļ│╝ ņĢ×ņ£╝ļĪ£ņØś Ļ│äĒÜŹ, ļ│┤ĒśĖņ×É ņĢłņŗ¼ņŗ£ĒéżĻĖ░ Ēś╣ņØĆ ņĀĢļ│┤ ņĀäļŗ¼ĒĢśņŗ£ļ®┤ņä£ ļ®┤ļŗ┤ĒĢśļŖö Ļ▓āņØä ļ│┤Ļ│Ā, ĒÖśņ×Éļ¦łļŗż ļŗżļźĖ ņāØĻ░üņØä ĒĢśĻ│Ā ņ׳Ļ│Ā, ĻĘĖ ņĀÉņØä ņŚ╝ļæÉņŚÉ ļæÉĻ│Ā ĒÖśņ×É ļ│┤ĒśĖņ×ÉņŚÉ ļö░ļØ╝ ļ®┤ļŗ┤ĻĖ░ļ▓ĢņØä ļŗżļź┤Ļ▓ī ĒĢ┤ņĢ╝ ĒĢ£ļŗżļŖö ņĀÉņØä ļ░░ņøĀļŗż(reflection).ŌĆØ
Ļ░£ņØĖņĀü ņ×Éņ¦łņŚÉņä£ņØś ļĪż ļ¬©ļŹĖļ¦üņØś ļīĆņāüņØĆ ļīĆļČĆļČä ņĀäļ¼ĖņØśņŚÉņä£ ļéśĒāĆļé¼ļŗż(40Ļ▒┤, 72.73%). ļśÉĒĢ£ ļŗżļźĖ ļĪż ļ¬©ļŹĖļ¦ü ņŻ╝ņĀ£ļ│┤ļŗż ļÅÖļŻīļź╝ ļĪż ļ¬©ļŹĖļĪ£ ņé╝ņØĆ Ļ▓ĮņÜ░Ļ░Ć ļ¦ÄņĢśļŗż(9Ļ▒┤, 16.36%). ņĀäļ¼ĖņØśņŚÉ ļīĆĒĢ£ Ļ░£ņØĖņĀü ņ×Éņ¦łņØś ļĪż ļ¬©ļŹĖļ¦üņØĆ ņ¢┤ļĀżņÜ┤ ņāüĒÖ® ņåŹņŚÉņä£ ĻĖŹņĀĢņĀüņØĖ ņāØĻ░ü, ĻĄÉņ£Ī, ņŚ░ĻĄ¼, ņ¦äļŻīņŚÉ ļīĆĒĢ£ ņĀäļ¼Ėņ¦üņŚģņä▒ņŚÉ ļīĆĒĢ£ ņé¼ļ¬ģĻ░ÉĻ│╝ ņ¦äņŗżņä▒, ļŗżļźĖ Ļ│╝ņÖĆ ņāüĒśĖņ×æņÜ®ņŚÉņä£ņØś ļīĆņØĖĻ┤ĆĻ│ä ĻĖ░ņłĀ ļō▒ņØś ņāüĒÖ®ņŚÉņä£ ņØ╝ņ¢┤ļé¼ļŗż. ļÅÖļŻīņŚÉ ļīĆĒĢ£ ļĪż ļ¬©ļŹĖļ¦üņØĆ ņŚ┤ņĀĢņĀüņØ┤Ļ│Ā ņĀüĻĘ╣ņĀüņ£╝ļĪ£ ņ×äņāüņŗżņŖĄņŚÉ ņ░ĖņŚ¼ĒĢśļŖö ļ”¼ļŹöņŗŁ ņŖżĒé¼Ļ│╝ ĒāüņøöĒĢ£ ļ¬©ņŖĄņŚÉņä£ ņØ╝ņ¢┤ļé¼ļŗż(Table 3).
ļĪż ļ¬©ļŹĖ ļīĆņāüņØś Ļ░£ņØĖņĀü ņ×Éņ¦łņŚÉ ļīĆĒĢ£ ņä▒ņ░░ņłśņżĆņØä ļČäņäØĒĢ£ Ļ▓░Ļ│╝, ļ╣äĒīÉņĀü ņä▒ņ░░(20Ļ▒┤, 46.51%)Ļ│╝ ļŗ©ņł£ ņä▒ņ░░(15Ļ▒┤, 34.88%)ņØ┤ ļ¦ÄņĢśļŗż(Figure 2). ņØśļīĆņāØļōżņØ┤ ļŖÉļéĆ ļĪż ļ¬©ļŹĖņØś Ļ░£ņØĖņĀü ņ×Éņ¦łņØĆ ļĪż ļ¬©ļŹĖņØś ņØ╝ņŚÉ ļīĆĒĢ£ ņŚ┤ņĀĢ, ņ×ÉĻĖ░Ļ┤Ćļ”¼ ļ░Å ļ”¼ļŹöņŗŁ, ĒāüņøöĒĢ£ ļ¼ĖņĀ£ĒĢ┤Ļ▓░ļŖźļĀź ļō▒ņŚÉņä£ ņ×ÉņŻ╝ ļéśĒāĆļé¼ļŗż. Ļ░£ņØĖņĀü ņ×Éņ¦łņŚÉņä£ņØś ņä▒ņ░░ņłśņżĆņŚÉ ļö░ļźĖ ņśłņŗ£ļŖö ļŗżņØīĻ│╝ Ļ░Öļŗż. ļīĆļČĆļČä ĒĢÖņāØļōżņØś ļĪż ļ¬©ļŹĖņØś Ļ░£ņØĖņĀü ņ×Éņ¦łņŚÉ ļīĆĒĢ£ ļ╣äĒīÉņĀü ņä▒ņ░░Ļ│╝ ļŗ©ņł£ ņä▒ņ░░ņØä ĒåĄĒĢ┤ ņØ╝ņŚÉ ļīĆĒĢ£ ņé¼ļ¬ģĻ│╝ ĒŚīņŗĀ, ĒśĖĻĖ░ņŗ¼, ņ¦äņĀĢņä▒, ņŚ┤ņĀĢ ļō▒ ņ┤łņøöņĀüņØĖ ļé┤ļ®┤ņØś ņøÉņ╣ÖņØä ļ░░ņøī ļéśĻ░ł ņłś ņ׳ņŚłļŗż.
ŌĆ£ņØśļŻī, ĒĢÖņāØĻĄÉņ£Ī, ņØśĒĢÖ ĒāÉĻĄ¼ ļō▒ ņ¢┤ļŖÉ ĒĢśļéś ņåīĒÖĆĒ׳ ĒĢśņ¦Ć ņĢŖĻ│Ā ņŚ┤ņŗ¼Ē׳ ņ×äĒĢśņŗ£ļŖö ļ¬©ņŖĄņØ┤ ļ®ŗņ׳ņŚłļŗż. ņØśņé¼ļĪ£ņä£ Ļ░ł ņłś ņ׳ļŖö ņŚ¼ļ¤¼ĻĖĖņØä ļ¬©ļæÉ Ļ░ł ņłśļŖö ņŚåĻ▓Āņ¦Ćļ¦ī Ļ░üĻ░üņØś ĻĖĖņØ┤ ņ¢┤ļ¢ż ĻĖĖņØĖņ¦Ć ņĢīĻ│Ā ņ¦üņĀæ Ļ░Ćļ│┤ļ®┤ņä£ ĒāÉĻĄ¼ĒĢĀ ņłś ņ׳ļŖö ļŖźļĀźņØä ĻĖ░ļź┤Ļ│Ā ņŗČļŗż(critical reflection).ŌĆØ
ŌĆ£ĒŖĖļØ╝ņÜ░ļ¦ł ĒīīĒŖĖ ļŗ╣ņ¦üņØä ņä£ņŗ£ļŖö ļÅÖņĢł carotid artery rupture ĒÖśņ×ÉĻ░Ć ņ׳ļŖöļŹ░, ļ¦żņÜ░ ņ¢┤ļĀżņÜ┤ ņāüĒÖ®ņ×äņŚÉļÅä ņĄ£ņäĀņØä ļŗżĒĢ┤ ĒÖśņ×Éļź╝ ņé┤ļĀż ļé┤ņģ©ļŗż. ņāłļ▓Į ņŗ£Ļ░äļīĆņŚÉ ļ¦żņÜ░ ņ¦Ćņ╣£ ļ¬©ņŖĄņØ╝ ņłś ņ׳ņØīņŚÉļÅä ĒÖśņ×Éļź╝ ņÜ░ņäĀņŗ£ĒĢśļ®░ Ļ▒░ņØś ņŻĮņ¢┤Ļ░ĆļŖö ĒÖśņ×Éļź╝ ņé┤ļĀżļé┤ņ¢┤ ņĀĢņāü Ēć┤ņøÉĒĢśĻ▓ī ĒĢ£ ņĀÉņŚÉņä£ Ļ░Éļ¬ģļ░øņĢśļŗż(thoughtful action or intro-spection).ŌĆØ
ŌĆ£ņŗ¼ņןļé┤Ļ│╝ļź╝ ņĀäĻ│ĄĒĢśņģ©ņØīņŚÉļÅä ņ×ÉņŗĀņØ┤ Ļ┤Ćņŗ¼ ņ׳ļŖö ņØæĻĖēņØśĒĢÖņØä ļśÉ ļ░░ņÜ░Ļ│Ā ņØ┤ļź╝ ņÜ░ļ”¼ ļ│æņøÉņŚÉņä£ Ļ░£ņ▓ÖĒĢśņŗ£Ļ│Ā, ļśÉ ņÜ░ļ”¼ļéśļØ╝ņŚÉņä£ ņĀäļ¼ĖĻ░ĆļĪ£ņä£ ņØ┤ļ”äņØä ļ¢©ņ╣£ļŗż. Ļ┤Ćņŗ¼ņØ┤ ņ׳ļŖö ļČäņĢ╝ņŚÉ ņĀüĻĘ╣ņĀüņ£╝ļĪ£ ļŗżĻ░ĆĻ░Ć ļüŖņ×äņŚåņØ┤ ļ░░ņÜ░ļŖö ņ×ÉņäĖļź╝ ļ│┤ņĢśļŗż(habitual action & nonreflective).ŌĆØ
Ļ░Ćļź┤ņ╣śļŖö ĻĖ░ņłĀņŚÉņä£ņØś ļĪż ļ¬©ļŹĖļ¦üņØś ļīĆņāüņØĆ ļīĆļČĆļČä ņĀäļ¼ĖņØś(13Ļ▒┤, 59.09%)ņÖĆ ņĀäĻ│ĄņØś(8Ļ▒┤, 36.36%)ņśĆļŗż. ņĀäļ¼ĖņØśņŚÉ ļīĆĒĢ£ Ļ░Ćļź┤ņ╣śļŖö ĻĖ░ņłĀņŚÉņä£ņØś ļĪż ļ¬©ļŹĖļ¦üņØĆ ĒĢÖņāØļ┐Éļ¦ī ņĢäļŗłļØ╝ ņĀäĻ│ĄņØśļź╝ Ļ░Ćļź┤ņ╣Ā ļĢīļÅä ņ׳ņŚłņ£╝ļ®░, Ļ░Ćļź┤ņ╣©ņŚÉņä£ ĒĢÖņŖĄņ×ÉņŚÉ ļīĆĒĢ£ ņŚ┤ņĀĢĻ│╝ ļ░░ļĀż, ņ▓┤Ļ│äņĀüņØĖ Ļ░Ćļź┤ņ╣© ļō▒ņØ┤ ņ׳ņŚłļŗż. ņĀäĻ│ĄņØśļź╝ ļīĆņāüņ£╝ļĪ£ ĒĢĀ ļĢīļŖö Ļ│Āļģäņ░©Ļ░Ć ņĀĆļģäņ░©ļź╝ Ļ░Ćļź┤ņ╣Ā ļĢīļÅä ĒĢÖņŖĄņ×ÉņØś ņä▒ņןņŚÉ ļīĆĒĢ£ ĒŚīņŗĀĻ│╝ ĻĖŹņĀĢņĀüņØĖ Ļ┤ĆĻ│ä ĒśĢņä▒ņŚÉņä£ ļĪż ļ¬©ļŹĖļ¦üņØ┤ ņØ╝ņ¢┤ļé¼ļŗż(Table 4).
ņĀäļ¼ĖņØśņÖĆ ņĀäĻ│ĄņØśļź╝ ļīĆņāüņ£╝ļĪ£ ļŗ©ņł£ ņä▒ņ░░(11Ļ▒┤, 50.00%)Ļ│╝ ļ╣äĒīÉņĀü ņä▒ņ░░(6Ļ▒┤, 27.27%)ņØ┤ Ļ░Ćņן ļ¦ÄņĢśļŗż(Figure 3). Ļ░Ćļź┤ņ╣śļŖö ĻĖ░ņłĀņŚÉņä£ņØś ņä▒ņ░░ņłśņżĆņŚÉ ļö░ļźĖ ņśłņŗ£ļŖö ļŗżņØīĻ│╝ Ļ░Öļŗż. ļīĆļČĆļČä ņØśļīĆņāØļōżņØĆ ļŗ©ņł£ ņä▒ņ░░Ļ│╝ ļ╣äĒīÉņĀü ņä▒ņ░░ņØä ĒåĄĒĢ┤ ņ×äņāüĻĄÉņ£Īņ×ÉņØś ĒĢÖņŖĄņ×É ņżæņŗ¼ņØś Ļ░Ćļź┤ņ╣śļŖö ĻĖ░ņłĀĻ│╝ ĒĢÖņŖĄņ×ÉņÖĆņØś ĻĖŹņĀĢņĀüņØĖ Ļ┤ĆĻ│ä ĻĄ¼ņČĢĻ│╝ ņä▒ņןņØś ļÅäņøĆņØä ņŻ╝ļŖö ĻĄÉņ£Īņ×ÉņŚÉ ļīĆĒĢ£ ĻĖŹņĀĢņĀüņØĖ ļĪż ļ¬©ļŹĖļ¦üņØä Ļ▓ĮĒŚśĒĢśņśĆļŗż.
ŌĆ£ņ¢┤ļĀżņÜ┤ ņ¦łļ¼ĖņØ┤ ļ¦ÄĻĖ░ļĪ£ ņ£Āļ¬ģĒĢ£ ĻĄÉņłśļŗś ņÖĖļלļź╝ ļōżņ¢┤Ļ░ĆĻĖ░ ņĀäņŚÉ ņĀäĻ│ĄņØś ņäĀņāØļŗśĻ╗śņä£ ņ▓┤Ļ│äņĀüņ£╝ļĪ£ Ēŗ░ņ╣ŁņØä ĒĢ┤ņŻ╝ņģ©ļŗż. ļéś ļśÉĒĢ£ Ēøäļ░░ļōżņŚÉĻ▓ī ņĢīĻĖ░ ņēĮĻ▓ī ņäżļ¬ģĒĢ┤ņżä ņłś ņ׳ņØä ļ¦īĒü╝ ņŚ┤ņŗ¼Ē׳ Ļ│ĄļČĆĒĢ┤ņĢ╝Ļ▓Āļŗż. ņ¦ĆņŗØņØä ļéśļłäļŖö Ļ▓āņŚÉ ņØĖņāēĒĢśņ¦Ć ņĢŖņØĆ ņØśņé¼Ļ░Ć ļÉśņ¢┤ņĢ╝Ļ▓Āļŗż(critical reflection).ŌĆØ
ŌĆ£ĒלļōĀ ņŖżņ╝Ćņżä ņÖĆņżæņŚÉļÅä ĒĢÖņāØļōżņŚÉĻ▓ī Ļ┤Ćņŗ¼ņØä Ļ░ĆņĀĖņŻ╝ņŗ£Ļ│Ā, presentation, teaching ĒĢ┤ņŻ╝ņŗ£Ļ│Ā ĒؼņāØņĀüņØĖ ļ¬©ņŖĄņØä ļ│┤ņśĆļŗż. ĒÖśņ×É ĒżĒĢ©ĒĢ┤ ļ¬©ļōĀ ņŻ╝ļ│Ć ņé¼ļ×īļōżņŚÉĻ▓ī Ļ┤Ćņŗ¼ņØä Ļ░ĆņĀĖņŻ╝Ļ│Ā ņä▒ņØś ņ׳Ļ│Ā ņ▒ģņ×äņØä Ļ░¢Ļ│Ā ļīĆĒĢśļŖö Ļ▓āņØä ļ░░ņøĀļŗż(thoughtful action or intro-spection).ŌĆØ
ŌĆ£ņŗżņŖĄņŚÉņä£ ņśłņÖĖ ņ╝ĆņØ┤ņŖżļź╝ ļ│┤ņŚ¼ņŻ╝ņŗ£Ļ▒░ļéś typicalĒĢ£ ņ╝ĆņØ┤ņŖżļź╝ ļ│┤ņŚ¼ņŻ╝ņŗ£ļŖö Ļ▓āņØä ļ│┤ļ®░, typicalĒĢ£ Ļ▓āĻ│╝ exceptionalĒĢ£ Ļ▓āņØä ļÅÖņŗ£ņŚÉ ņĢīņĢäļæÉĻ│Ā ņ¦äļŗ©Ļ│╝ņĀĢ ņżæņŚÉ ĒĢäņÜöĒĢ£ Ļ▓āņØ┤ ņ¢┤ļ¢ż Ļ▓āņØ┤Ļ│Ā, ņ¢┤ļ¢ż Ļ▓āņØä ŌĆśĻĘĖļ¤┤ ņłśļÅä ņ׳ļŗżŌĆÖļØ╝Ļ│Ā ņāØĻ░üĒĢĀ ņłś ņ׳ļŖö ņŚ¼ņ£Āļź╝ ņĀäļŗ¼ļ░øņØä ņłś ņ׳ņŚłļŗż(habitual action & nonreflective).ŌĆØ
ļČĆņĀĢņĀüņØĖ ļĪż ļ¬©ļŹĖļ¦üņØś ļīĆņāüņØĆ ļīĆļČĆļČä ņĀäļ¼ĖņØś(29Ļ▒┤, 64.44%)ņśĆņ£╝ļ®░, ņĀäĻ│ĄņØś(9Ļ▒┤, 20%), Ļ░äĒśĖņé¼(4Ļ▒┤, 8.89%), ļÅÖļŻī(3Ļ▒┤, 6.67%)ņŚÉņä£ ļéśĒāĆļé¼ļŗż. ĻĄÉņłśņÖĆ ņĀäļ¼ĖņØśņŚÉ ļīĆĒĢ£ ļČĆņĀĢņĀüņØĖ ļĪż ļ¬©ļŹĖļ¦üņØĆ ņ¦äļŻī ņŗ£ ĒÖśņ×Éļź╝ ņĪ┤ņżæĒĢśņ¦Ć ņĢŖļŖö ļ¬©ņŖĄĻ│╝, Ēŗ░ņ╣Ł ņŗ£ ņØśļīĆņāØņŚÉ ļīĆĒĢ£ ļČĆļŗ╣ĒĢ£ ļīĆņÜ░ ļō▒ņØ┤ Ļ│ĄĒåĄņĀüņØĖ ņāüĒÖ®ņØ┤ņŚłļŗż. ņĢäņÜĖļ¤¼ Ļ░äĒśĖņé¼Ļ░Ć ĒÖśņ×ÉņÖĆ ņØśļīĆņāØņŚÉ ļīĆĒĢ£ ĒŚśļŗ┤ ļ░Å ĒÖśņ×Éļź╝ ļīĆĒĢĀ ļĢī ņĪ┤ņżæĒĢśņ¦Ć ņĢŖļŖö ļ¬©ņŖĄņŚÉņä£ ļČĆņĀĢņĀüņØĖ ļĪż ļ¬©ļŹĖļ¦üņØä Ļ▓ĮĒŚśĒĢśņśĆļŗż(Table 5).
ļ╣äĒīÉņĀü ņä▒ņ░░Ļ│╝ ļŗ©ņł£ ņä▒ņ░░ņØś ļ╣äņ£©ņØ┤ ļŗżļźĖ ļĪż ļ¬©ļŹĖļ¦ü ņāüĒÖ®ļ│┤ļŗż ļ¦ÄņĢśļŗż(Figure 4). ļČĆņĀĢņĀü ļĪż ļ¬©ļŹĖļ¦üņØś ņä▒ņ░░ņłśņżĆņŚÉ ļö░ļźĖ ņśłņŗ£ļŖö ļŗżņØīĻ│╝ Ļ░Öļŗż. ļīĆļČĆļČä ņØśļīĆņāØļōżņØĆ ļ╣äĒīÉņĀü ņä▒ņ░░Ļ│╝ ļŗ©ņł£ ņä▒ņ░░ņØä ĒåĄĒĢ┤ ļĪż ļ¬©ļŹĖņØś ļČĆņĀĢņĀü Ē¢ēļÅÖņŚÉ ļīĆĒĢ┤ ĻĘĖļīĆļĪ£ ļ░øņĢäļōżņØ┤ļŖö Ļ▓āņØ┤ ņĢäļŗłļØ╝, ĒĢśņ¦Ć ļ¦ÉņĢäņĢ╝ ĒĢśļŖö Ē¢ēļÅÖņ£╝ļĪ£ ņØĖņŗØĒĢśĻ│Ā, ĻĖŹņĀĢņĀü ļĪż ļ¬©ļŹĖņŚÉ ļīĆĒĢ£ ņżæņÜöņä▒ņØä Ļ░ĢĒĢśĻ▓ī ņØĖņŗØĒĢśņśĆļŗż.
ŌĆ£ĒÖśņ×ÉņŚÉĻ▓ī ļ¦ēļ¦ÉĒĢśĻ│Ā ĒÖśņ×Éļź╝ ņ£äĒĢ┤ ĒśĖĒåĄ ņ╣śļŖö Ļ▓ā Ļ░ÖņØ┤ ļ│┤ņØ┤ņ¦Ćļ¦ī ĒÖöĒÆĆņØ┤ļź╝ ĒĢśļŖö Ļ▓āņ▓śļ¤╝ ļ│┤ņśĆļŗż. ĒÖśņ×ÉĻ░Ć ņ╣śļŻīļ░®ņ╣©ņØä ļö░ļź┤ņ¦Ć ņĢŖļŹöļØ╝ļÅä, ņØ┤ļź╝ ņäżļōØĒĢśĻ│Ā ņØ┤ĒĢ┤ņŗ£ņ╝£ ņØśĻ▓¼ ņ░©ņØ┤ļź╝ ņóüĒśĆĻ░ł ļĢī ņāüļīĆļź╝ ņĪ┤ņżæĒĢ┤ņŻ╝ļŖö ņ×ÉņäĖĻ░Ć ĒĢäņÜöĒĢśļŗżĻ│Ā ņāØĻ░üĒ¢łļŗż(reflection).ŌĆØ
ŌĆ£ĻĄÉņłśļŗśĻ╗śņä£ ņØ╝ņØä ĒĢśņŗ£ļŹś ņżæ ĒÖśņ×ÉĻ░Ć ņלļ¬╗ļÉ£ ņØ╝ņØ┤ ņ׳ņŚłļŖöļŹ░, ļ│ĖņØĖņØ┤ ņŻ╝ļÅäļź╝ ĒĢśņŚ¼ ĒÖśņ×Éļź╝ ļ│┤ņĢśņØīņŚÉļÅä ļČłĻĄ¼ĒĢśĻ│Ā, ņśåņŚÉ ņ׳ļŹś Ļ░äĒśĖņé¼ņÖĆ ņĀäĻ│ĄņØś ņäĀņāØļŗśĻ╗ś ĒÖöļź╝ ļé┤ļ®░ ĒāōņØä Ē¢łļŗż. ļé© ĒāōĒĢśļ®┤ ļÅäņøĆļÅä ņĢł ļÉśĻ│Ā ņĀĢļ¦É ņĢł ņóŗņĢä ļ│┤ņØĖļŗż(thoughtful action or introspection).ŌĆØ
ņäĀĒ¢ēņŚ░ĻĄ¼ņŚÉņä£ ņĀĢļ”¼ļÉ£ ļĪż ļ¬©ļŹĖļ¦üņØś ĒŖ╣ņä▒Ļ│╝ ņä▒ņ░░ņłśņżĆņØś Ļ░£ļģÉņØä ļ░öĒāĢņ£╝ļĪ£ ĻĄŁļé┤ ņØ╝Ļ░£ ņØśĻ│╝ļīĆĒĢÖ 4ĒĢÖļģä ĒĢÖņāØņØä ļīĆņāüņ£╝ļĪ£ ņ×äņāüņŗżņŖĄ ņżæ Ļ▓ĮĒŚśĒĢ£ ļĪż ļ¬©ļŹĖļ¦üĻ│╝ ņä▒ņ░░ņłśņżĆņØä ļČäņäØĒĢ£ Ļ▓░Ļ│╝, ņ×äņāüņŗżņŖĄņŚÉ ņ░ĖņŚ¼ĒĢ£ ĒĢÖņāØļōżņØĆ ļ»Ėļל ņ×ÉņŗĀļōżņØś ļ¬©ņŖĄņØĖ ņØśņé¼ļź╝ ļĪż ļ¬©ļŹĖļĪ£ ņ×ÉņŻ╝ ņāØĻ░üĒĢśļ®░, ĒŖ╣Ē׳ ņĀäļ¼ĖņØśņØś ņ×äņāüņĀü Ēā£ļÅäņŚÉņä£ ļĪż ļ¬©ļŹĖļ¦üņØä Ļ░Ćņן ļ¦ÄņØ┤ Ļ▓ĮĒŚśĒ¢łļŗż. ņĢäņÜĖļ¤¼ ļČĆņĀĢņĀüņØĖ ļĪż ļ¬©ļŹĖļ¦üņØś ļīĆņāüļÅä ņĀäļ¼ĖņØśĻ░Ć Ļ░Ćņן ļ¦ÄņĢśļŗż. ņ×äņāüņŗżņŖĄ ņżæ ņØśļīĆņāØņØś ļĪż ļ¬©ļŹĖļ¦ü Ļ▓ĮĒŚśĻ│╝ ņä▒ņ░░ņłśņżĆņØä ĒåĄĒĢ┤ ņŚ░ĻĄ¼ņ¦äļōżņØś ņØ╝ņ░©ņĀü Ļ┤Ćņŗ¼ņØĆ ņ×äņāü ĻĄÉņ£Īņ×ÉļōżņØ┤ ļĪż ļ¬©ļŹĖļ¦üņŚÉ ļīĆĒĢ£ ņżæņÜöņä▒ņØä ņØĖņŗØĒĢśĻ│Ā, ĻĖŹņĀĢņĀü ļĪż ļ¬©ļŹĖļ¦ü Ļ▓ĮĒŚśņØä ņØśļīĆņāØņŚÉĻ▓ī ņĀ£Ļ│ĄĒĢśĻĖ░ ņ£äĒĢ£ ĻĄÉņ£ĪĒöäļĪ£ĻĘĖļש Ļ░£ļ░£ņŚÉ ļīĆĒĢ£ ĻĖ░ņ┤łņ×ÉļŻīļź╝ ņĀ£Ļ│ĄĒĢśļŖö Ļ▓āņØ┤ņŚłļŗż. ņØ┤ļź╝ ļ░öĒāĢņ£╝ļĪ£ ļÅäņČ£ĒĢ£ Ļ│Āņ░░ņØĆ ļŗżņØīĻ│╝ Ļ░Öļŗż.
ņ▓½ņ¦Ė, ņĪ░ņ¦ü ņ░©ņøÉņŚÉņä£ ņĀäļ¼ĖņØśņÖĆ ņĀäĻ│ĄņØśļź╝ ļīĆņāüņ£╝ļĪ£ ļĪż ļ¬©ļŹĖļ¦ü Ļ░ĢĒÖöļź╝ ņ£äĒĢ£ ĻĄÉņłśĻ░£ļ░£ĒöäļĪ£ĻĘĖļשņØ┤ ņ▓┤Ļ│äņĀüņ£╝ļĪ£ Ļ░£ļ░£ļÉśņ¢┤ņĢ╝ ĒĢ£ļŗż. ņ×äņāüņŗżņŖĄņŚÉ ņ░ĖņŚ¼ĒĢ£ ņØśļīĆņāØļōżņØĆ ņĀäļ¼ĖņØśņÖĆ ņĀäĻ│ĄņØśļź╝ ļīĆņāüņ£╝ļĪ£ ļĪż ļ¬©ļŹĖļ¦üņØ┤ Ļ░Ćņן ļ¦ÄņØ┤ ņØ╝ņ¢┤ļé¼ļŗż. ņĀäļ¼ĖņØśņÖĆ ņĀäĻ│ĄņØśļŖö ņ×äņāüņŗżņŖĄ Ļ│╝ņĀĢņŚÉņä£ ņØśļīĆņāØļōżĻ│╝ Ļ░Ćņן ļ¦ÄņØĆ ņŗ£Ļ░äņØä ļ│┤ļé┤ļŖö ĻĄÉņ£Īņ×ÉļĪ£ņä£ ņØśļīĆņāØļōżņØś ņĀäļ¼Ėņ¦ü ņĀĢņ▓┤ņä▒ ĒśĢņä▒ņŚÉ Ļ░Ćņן Ēü░ ņśüĒ¢źņØä ņŻ╝ļŖö ņĪ┤ņ×¼ņ×äņØä ņŗ£ņé¼ĒĢ£ļŗż. ņØ┤ļŖö ņØśļīĆņāØļōżņØĆ ņäĀļ░░ ņØśņé¼, ņ×äņāü ņØśņé¼ ļō▒ ņ×äņāü ĻĄÉņ£Īņ×ÉļĪ£ļČĆĒä░ ņØśņé¼ņØś ĒĢäņłśņĀüņØĖ ņŚŁĒĢĀĻ│╝ ĒŖ╣ņ¦ĢņØä ĒīīņĢģĒĢśļ®░, ĻĄÉņ£Īņ×ÉļōżņØś Ē¢ēļÅÖĻ│╝ Ēā£ļÅä ļō▒ņØä Ļ┤Ćņ░░ĒĢśĻ│Ā ņä▒ņ░░ĒĢśļŖö Ļ│╝ņĀĢņŚÉņä£ ņĀäļ¼Ėņ¦ü ņĀĢņ▓┤ņä▒ņØä ĒśĢņä▒ĒĢ┤ ļéśĻ░äļŗżļŖö ĻĖ░ņĪ┤ ņŚ░ĻĄ¼Ļ▓░Ļ│╝ņÖĆ ņØ╝ņ╣śĒĢ£ļŗż[28]. ĒŖ╣Ē׳ ņĀäļ¼ĖņØśņÖĆ ĒÖśņ×ÉņØś ņāüĒśĖņ×æņÜ®ņŚÉņä£ ņåīĒåĄĻ│╝ Ļ│ĄĻ░ÉņĀü Ļ▓Įņ▓Ł, ņ╣£ņĀłĒĢ£ Ēā£ļÅäņÖĆ Ļ░ÖņØĆ ņ×äņāüņĀü Ēā£ļÅä, ņ×ÉĻĖ░Ļ┤Ćļ”¼, ļīĆņØĖĻ┤ĆĻ│äņÖĆ Ļ░ÖņØĆ Ļ░£ņØĖņĀü ņ×Éņ¦ł, Ēŗ░ņ╣Ł ņŖżĒé¼ ļō▒ņŚÉņä£ ņØśļīĆņāØļōżņØĆ ļåÆņØĆ ņä▒ņ░░ņØä ļ│┤ņśĆļŗż. ļö░ļØ╝ņä£ ņ×äņāü ĻĄÉņ£Īņ×ÉļōżņØä ļīĆņāüņ£╝ļĪ£ ņ×äņāüņĀü Ēā£ļÅä, Ļ░£ņØĖņĀü ņ×Éņ¦ł, Ļ░Ćļź┤ņ╣śļŖö ĻĖ░ņłĀ, ļČĆņĀĢņĀüņØĖ ļĪż ļ¬©ļŹĖļ¦üņŚÉ ļīĆĒĢ£ ļ╣äĒīÉņĀü ņä▒ņ░░ ļō▒ņØä ņŻ╝ņĀ£ļĪ£ ņ▓┤Ļ│äņĀüņØĖ ĻĄÉņłśĻ░£ļ░£ņØä ņ£äĒĢ£ ĒöäļĪ£ĻĘĖļשņØ┤ ĒĢäņÜöĒĢśļŗż. ņØ┤ļŖö ņØśļīĆņāØļōżņØś ņĀäļ¼Ėņ¦üņŚģņä▒ ĒśĢņä▒Ļ│╝ Ļ░£ļ░£, ĻĘĖļōżņØś ņłśĒ¢ēļŖźļĀźņŚÉļÅä ĻĖŹņĀĢņĀüņØĖ ņśüĒ¢źņØä ļ»Ėņ╣Ā ņłś ņ׳ļÅäļĪØ ņäżĻ│äļÉśņ¢┤ņĢ╝ ĒĢ£ļŗż[29]. ļśÉĒĢ£ ĻĖŹņĀĢņĀüņØĖ ļĪż ļ¬©ļŹĖļ¦ü ĻĄÉņłśĻ░£ļ░£ĒöäļĪ£ĻĘĖļשņØĆ ņ×äņāüĻĄÉņ£Īņ×Éļź╝ ļäśņ¢┤ ņĀäĻ│ĄņØś, ņ¦üņóģĻ░ä ĻĄÉņ£Īņ£╝ļĪ£ ĒÖĢņןĒĢśļŖö Ļ▓āņØä ņĀ£ņĢłĒĢ£ļŗż.
ļæśņ¦Ė, ņ×äņāüņŗżņŖĄņŚÉ ņ░ĖņŚ¼ĒĢ£ ņØśļīĆņāØļōżņØĆ ņĀäļ¼ĖņØśņØś ņ×äņāüņĀü Ēā£ļÅäņŚÉņä£ Ļ░Ćņן ļåÆņØĆ ņłśņżĆņØś ĻĖŹņĀĢņĀü ļĪż ļ¬©ļŹĖļ¦üņØä Ļ▓ĮĒŚśĒĢ£ļŗż. ņ×äņāüņĀü Ēā£ļÅäļŖö ņØśņé¼ņÖĆ ĒÖśņ×ÉņÖĆņØś ņāüĒśĖņ×æņÜ® ņåŹņŚÉņä£ ļØ╝Ēż ĒśĢņä▒Ļ│╝ ņĪ┤ņżæ, Ļ│ĄĻ░É, ļÅÖņĀĢ ļō▒ņŚÉņä£ ļéśĒāĆļé£ļŗż. ņØ┤ļŖö ņäĀĒ¢ēņŚ░ĻĄ¼ņŚÉņä£ ļČäļźśĒĢ£ ņØśņé¼ņØś ĻĖŹņĀĢņĀü ļĪż ļ¬©ļŹĖļ¦ü ņżæ ņ×äņāüņĀü Ēā£ļÅäņØś ĒŖ╣ņä▒Ļ│╝ Ļ░ÖņĢśļŗż[9]. ņ×äņāü ĻĄÉņ£Īņ×ÉļŖö ņ×äņāüņŗżņŖĄ ņżæ ĒÖśņ×Éļź╝ ļ¦łņŻ╝ĒĢśĻ│Ā, ņ¦äļŻīĒĢśļŖö ņł£Ļ░äņŚÉ ļĪż ļ¬©ļŹĖļ¦üņØ┤ ņØ╝ņ¢┤ļéśļŖö ņł£Ļ░äņ×äņØä ņØśļÅäņĀüņ£╝ļĪ£ ņØĖņŗØĒĢ┤ņĢ╝ ĒĢśļ®░, ļĪż ļ¬©ļŹĖļĪ£ņä£ ņŖżņŖżļĪ£ļź╝ ņØĖņŗØĒĢśĻ│Ā, ņä▒ņ░░ĒĢśĻ│Ā, ņ×ÉĻĖ░ĒåĄņĀ£ļŖźļĀźņØä Ļ░£ļ░£ĒĢĀ ĒĢäņÜöņä▒ņØ┤ ņ׳ļŗż[11]. ņĢäņÜĖļ¤¼ ĒÖśņ×ÉņÖĆ ņØśņé¼ņØś Ļ┤ĆĻ│ä ņåŹņŚÉņä£ ņØĖĻ░äļŗżņÜ┤ ļ¬©ņŖĄņØä ļ│┤ņØ╝ ļĢī ĒĢÖņāØļōżņØĆ ņóŗņØĆ ņØśņé¼ļĪ£ņä£ Ļ░ĢĒĢśĻ│ĀļÅä ĻĖŹņĀĢņĀüņØĖ ļĪż ļ¬©ļŹĖļ¦üņØä Ļ▓ĮĒŚśĒĢ£ļŗżļŖö Ļ▓āņØä ņØĖņŗØĒĢ┤ņĢ╝ ĒĢ£ļŗż[15,16]. ļö░ļØ╝ņä£ ņ×äņāü ĻĄÉņ£Īņ×ÉļōżņØś ņØśņé¼ņåīĒåĄĻĖ░ņłĀ, ĒÖśņ×ÉņÖĆ ņØśņé¼ņØś ņāüĒśĖņ×æņÜ® ļō▒ ņĀäļ¼Ėņ¦ü ņĀĢņ▓┤ņä▒ ĒśĢņä▒ ĻĄÉņ£ĪņØä ņ£äĒĢ┤ ņØśļŻīņØĖļ¼ĖĒĢÖ ĻĄÉņ£ĪĒöäļĪ£ĻĘĖļשņØ┤ ņĪ░ņ¦ü ņ░©ņøÉņŚÉņä£ ņןļĀżļÉśņ¢┤ņĢ╝ ĒĢ£ļŗż. ļśÉĒĢ£ Ļ░£ņØĖņØś ņ×ÉņĢä ļ░£ļŗ¼ ņłśņżĆņØ┤ ļŗżļź┤ĻĖ░ņŚÉ ļĪż ļ¬©ļŹĖļ¦üņŚÉ Ļ┤ĆĒĢ£ ĻĄÉņ£ĪĒöäļĪ£ĻĘĖļשņØĆ ļŗ©Ļ│äļ│äļĪ£ ņäżĻ│äĒĢśĻ│Ā ņÜ┤ņśüĒĢĀ ņłś ņ׳ņ£╝ļ®░, ĻĄÉņ£Ī ĒśĢĒā£ļŖö ņåīĻĘĖļŻ╣ ļŗ©ņ£äņØś ņŗżĒ¢ē Ļ│ĄļÅÖņ▓┤ļź╝ ĒśĢņä▒ĒĢśņŚ¼ ņןĻĖ░ņĀüņØĖ ņä▒ņ░░Ļ│╝ Ļ▓ĮĒŚśĒĢÖņŖĄņØä ĒåĄĒĢ┤ Ļ░£ņØĖņØś Ēā£ļÅä, ĻĖ░ņłĀ, Ē¢ēļÅÖņØś ļ│ĆĒÖöņŚÉ ņśüĒ¢źņØä ņŻ╝ļ®░, ņĪ░ņ¦üņØś ĒĢĄņŗ¼ Ļ░Ćņ╣śļź╝ ļé┤ļ®┤ĒÖöĒĢĀ ņłś ņ׳ļÅäļĪØ ņ┤ēņ¦äĒĢ┤ņĢ╝ ĒĢ£ļŗż.
ņģŗņ¦Ė, ņ×äņāüņŗżņŖĄ ņżæ ņØśļīĆņāØļōżņØĆ ņ×äņāü ĻĄÉņ£Īņ×ÉņØś ļČĆņĀĢņĀüņØĖ ļĪż ļ¬©ļŹĖļ¦üņØä Ļ▓ĮĒŚśĒĢĀ ļĢī Ļ░Ćņן ļ¦ÄņØĆ ļ╣äĒīÉņĀü ņä▒ņ░░ņØ┤ ņØ┤ļŻ©ņ¢┤ņ¦äļŗż. ļČĆņĀĢņĀüņØĖ ļĪż ļ¬©ļŹĖļ¦üņØĆ ņ×äņāü ĻĄÉņ£Īņ×ÉļōżņØ┤ ņ¦äļŻī ņŗ£ ĒÖśņ×Éļź╝ ņĪ┤ņżæĒĢśņ¦Ć ņĢŖļŖö Ēā£ļÅäļéś ņØśļīĆņāØņØ┤ļéś ņĀäĻ│ĄņØś, ĒÖśņ×É, ļŗżļźĖ ļÅÖļŻīļōżņØä ļ¼┤ņŗ£ĒĢśĻ│Ā ļČĆļŗ╣ĒĢ£ ļīĆņÜ░ļź╝ ĒĢĀ ļĢī ļéśĒāĆļé£ļŗż. ņØ┤ļŖö ņ×äņāü ĻĄÉņ£Īņ×ÉņŚÉ ļīĆĒĢ£ ļČĆņĀĢņĀüņØĖ ļĪż ļ¬©ļŹĖļ¦üņØĆ ņĀäļ¼Ėņ¦üņŚģņä▒ Ļ░£ļ░£Ļ│╝ņĀĢņŚÉņä£ ĒØöĒ׳ ļ│╝ ņłś ņ׳ļŖö ĒśäņāüņØ┤ļ®░, ļČĆņĀĢņĀüņØĖ ļĪż ļ¬©ļŹĖļ¦üņØĆ ĒĢÖņāØļōżņØ┤ Ēö╝ĒĢ┤ņĢ╝ ĒĢĀ Ē¢ēļÅÖņØä ļ░░ņÜ░ļŖöļŹ░ ĻĖŹņĀĢņĀüņØĖ ņśüĒ¢źņØä ļ»Ėņ╣£ļŗżļŖö ĻĖ░ņĪ┤ ņŚ░ĻĄ¼Ļ▓░Ļ│╝ņÖĆ ņØ╝ņ╣śĒĢ£ļŗż[30]. ļśÉĒĢ£ ļČĆņĀĢņĀüņØĖ ļĪż ļ¬©ļŹĖļ¦üņØĆ ļ╣äĻ│ĄņŗØ ļśÉļŖö ņ×Āņ×¼ņĀü ĻĄÉņ£ĪĻ│╝ņĀĢņŚÉņä£ ļ░£ņāØĒĢśļ®░, ņ×äņāüĒÖśĻ▓ĮņŚÉņä£ ņāüļīĆļ░®ņŚÉĻ▓ī Ļ▓Įļ®ĖņĀüņØĖ ņ¢Ėņ¢┤ļź╝ ņé¼ņÜ®ĒĢĀ ļĢī ņØśļīĆņāØļōżņØĆ ļ¬©ļ░®ĒĢ┤ņä£ļŖö ņĢłļÉśļŖö Ļ░ĢĒĢ£ ņä▒ņ░░ņØä Ļ▓ĮĒŚśĒĢ£ļŗżļŖö ĻĖ░ņĪ┤ ņŚ░ĻĄ¼Ļ▓░Ļ│╝ļź╝ ļÆĘļ░øņ╣©ĒĢĀ ņłś ņ׳ļŗż[9]. ļö░ļØ╝ņä£ ĒĢÖņāØļōżņØ┤ ļ¼┤ļ╣äĒīÉņĀüņ£╝ļĪ£ ļĪż ļ¬©ļŹĖņØä ļ¬©ļ░®ĒĢśĻ▒░ļéś ĻĄÉņ£Īņ×ÉņØś ļ╣äņ£żļ”¼ņĀü Ē¢ēļÅÖņŚÉ ļīĆĒĢ┤ ļČĆņĀĢņĀüņØĖ ņśüĒ¢źņØä ļ░øļŖö Ļ▓āņØä ļ¦ēĻĖ░ ņ£äĒĢ┤ ņĪ░ņ¦ü ņ░©ņøÉņŚÉņä£ ĻĄÉņłśņ×ÉņÖĆ ĒĢÖņāØļōżņØä ļīĆņāüņ£╝ļĪ£ ļĪż ļ¬©ļŹĖļ¦üņŚÉ ļīĆĒĢ£ ļ╣äĒīÉņĀü ņłśņżĆņØś ņä▒ņ░░ ĻĄÉņ£ĪņØä Ļ░ĢĒÖöĒĢśļŖö ļŹ░ ļģĖļĀźĒĢ┤ņĢ╝ ĒĢ£ļŗż[21]. ļ╣äĒīÉņĀü ņä▒ņ░░ņØĆ ņä▒ņ░░ņłśņżĆ ņżæ Ļ░Ćņן ļåÆņØĆ ļŗ©Ļ│äņØ┤ļ®░, ĻĖ░ņĪ┤ņØś Ļ░Ćņ╣ś, ņŗĀļģÉņØä ĒÖĢņØĖĒĢśĻ▒░ļéś ļ│ĆĒÖśĒĢśņŚ¼ ļ»ĖļלņØś Ē¢ēļÅÖņØä ņØ┤ļüī ņłś ņ׳ļŖö ĒåĄņ░░ļĀźņØä ņŻ╝ĻĖ░ ļĢīļ¼ĖņØ┤ļŗż[26]. ļ░śļ®┤, Ļ░£ņØĖņØś ņä▒ņ░░ņłśņżĆņØĆ ņØ┤ņĀä Ļ▓ĮĒŚś ņāüĒā£ņÖĆ ņéČņØś Ļ░Ćņ╣śĻ┤Ć, Ēśäņ×¼ņØś ņéČņØś ņāüĒÖ®ņŚÉ ļö░ļØ╝ ļŗżļź╝ ņłśļÅä ņ׳ņ¦Ćļ¦ī, ĻĄÉņłśņ×ÉņÖĆ ĒĢÖņŖĄņ×ÉļōżņØ┤ ņ×ÉņŗĀņØś ņä▒ņ░░ņłśņżĆņØ┤ ņ¢┤ļŖÉ ļŗ©Ļ│äņØĖņ¦Ć ņØĖņŗØĒĢśĻ│Ā, ļ╣äĒīÉņĀü ņä▒ņ░░ņłśņżĆĻ╣īņ¦Ć ļÅäļŗ¼ĒĢĀ ņłś ņ׳ļÅäļĪØ ĻĄÉņ£ĪĒĢśļŖö Ļ▓āņØĆ ņżæņÜöĒĢśļŗż. ĒÜ©Ļ│╝ņĀüņØĖ ņä▒ņ░░ĻĄÉņ£ĪņØä ņ£äĒĢ£ ĻĄÉņłśĒĢÖņŖĄņĀäļץņØĆ ĻĖŹņĀĢņĀüņØĖ ļĪż ļ¬©ļŹĖļ¦üņŚÉ ļīĆĒĢ£ ĒöäļĀłņ×äņØä ņĀ£ņŗ£ĒĢśĻ│Ā, ņ×ÉņŗĀņØś ļĪż ļ¬©ļŹĖļ¦ü Ļ▓ĮĒŚśņØä ļ░öĒāĢņ£╝ļĪ£ ĒĢ£ ņä▒ņ░░ļ│┤Ļ│Āņä£ņÖĆ ļé┤ļ¤¼Ēŗ░ļĖī ļ░®ņŗØņØś ĻĖĆņō░ĻĖ░, ņ×ÉņĢäņØĖņŗØĒāÉĒŚś, Ēö╝ļō£ļ░▒Ļ│╝ ņĮöņ╣ŁņØä ĒåĄĒĢ£ ĻĖ░ņłĀ Ļ░ĢĒÖö, ņé¼ļĪĆ ļ░£Ēæ£ ļō▒ Ļ░£ņØĖņØś ņä▒ņ░░Ļ▓ĮĒŚśņØä Ēæ£ĒśäĒĢśĻ│Ā ļéśļłäļŖö ļ░®ņŗØņØä ņĀ£ņĢłĒĢ£ļŗż.
ļäĘņ¦Ė, ļČĆņĀĢņĀüņØĖ ļĪż ļ¬©ļŹĖļ¦üņØĆ ĒāĆ ņ¦üņóģ ņé¼ņØ┤ņŚÉņä£ļÅä ļ╣łļ▓łĒĢśĻ▓ī ņØ╝ņ¢┤ļé£ļŗż. ņØ┤ ņŚ░ĻĄ¼ņŚÉņä£ Ļ░äĒśĖņé¼ļź╝ ļīĆņāüņ£╝ļĪ£ ņØśļīĆņāØļōżņØĆ ļ╣äĒīÉņĀü ņä▒ņ░░ņłśņżĆņØś ļČĆņĀĢņĀüņØĖ ļĪż ļ¬©ļŹĖļ¦üņØä Ļ▓ĮĒŚśĒ¢łļŗż. ņØ┤ļŖö ņäĀĒ¢ēņŚ░ĻĄ¼ņŚÉņä£ ņØśļīĆņāØņØĆ ļŗżļźĖ ņĀäļ¼Ėņ¦üĻ│╝ ņāüĒśĖņ×æņÜ®ņØä ĒĢśļŖöļŹ░, ļČĆņĀĢņĀüņØĖ ļĪż ļ¬©ļŹĖļ¦üņØĆ Ļ░äĒśĖņé¼ņÖĆ ĒĢÖņāØĻ░äņØś ņāüĒśĖņ×æņÜ®ņŚÉņä£ ļéśĒāĆļéĀ ņłś ņ׳ļŗżļŖö Ļ▓░Ļ│╝ļź╝ ļÆĘļ░øņ╣©ĒĢ£ļŗż[31]. ļö░ļØ╝ņä£ ĒāĆ ņ¦üņóģ Ļ░äņØś ņłśĒÅēņĀü Ļ┤ĆĻ│äņÖĆ ņāüĒśĖ ņĪ┤ņżæņØä ņ┤ēņ¦äĒĢĀ ņłś ņ׳ļŖö ļ¼ĖĒÖöļź╝ ĒśĢņä▒ĒĢśĻ│Ā, Ļ░äĒśĖņé¼ļōżņØĆ Ļ░äĒśĖĒĢÖĻ│╝ ĒĢÖņāØļ┐Éļ¦ī ņĢäļŗłļØ╝ ņØśļīĆņāØļōżņŚÉĻ▓īļÅä ņ×ÉņŗĀņØ┤ ļĪż ļ¬©ļŹĖļ¦üņØ┤ ļÉĀ ņłś ņ׳ņØīņØä ņØĖņŗØĒĢśļŖö Ļ▓āņØ┤ ņżæņÜöĒĢśļŗż.
ņØ┤ ņŚ░ĻĄ¼ņØś ņĀ£ĒĢ£ņĀÉņØĆ ļŗżņØīĻ│╝ Ļ░Öļŗż. ņÜ░ņäĀ, ņØ┤ ņŚ░ĻĄ¼ļŖö ņ×äņāüņŗżņŖĄņŚÉ ņ░ĖņŚ¼ĒĢ£ ņØśļīĆņāØļōżņŚÉĻ▓ī ļĪż ļ¬©ļŹĖĻ│╝ ļĪż ļ¬©ļŹĖļ¦üņŚÉ ļīĆĒĢ£ Ļ░£ļģÉņØä ņäżļ¬ģĒĢśĻ│Ā, ņ×ÉņŗĀņØś Ļ▓ĮĒŚśņØä ĻĖĆļĪ£ņŹ© Ēæ£ĒśäĒĢśļÅäļĪØ ĒĢśņśĆļŗż. ĒĢÖņāØļōżņØĆ ņØĄļ¬ģņä▒ņØä ļ│┤ņן ļ░øĻ│Ā, ņ×ÉņŗĀņØś Ļ▓ĮĒŚśņØä ĒÄĖņĢłĒĢśĻ▓ī ņĀüņØä ņłś ņ׳ņŚłņ£╝ļ®░, ņä▒ņ░░ļ│┤Ļ│Āņä£ļŖö ņĀĢņ¦üĒĢśĻ│Ā, ĒÄĖĒ¢źļÉśņ¦Ć ņĢŖņĢśļŗżļŖö ņĀÉņŚÉņä£ ņןņĀÉņØ┤ ņ׳ļŗż. ĒĢśņ¦Ćļ¦ī ņØ┤ļŖö ĒÅēņåī ļĪż ļ¬©ļŹĖņŚÉ ļīĆĒĢ┤ ļŖÉļü╝ļŖö ņ╣£ļ░ĆļÅäļéś Ļ┤ĆĻ│äņŚÉ ļö░ļØ╝ ļŗ¼ļØ╝ņ¦ł ņłś ņ׳ļŗż. ļæśņ¦Ė, ĒĢÖņāØ Ļ░£ņØĖņØś ņä▒ņ░░ņŚŁļ¤ēņØä Ļ▓Ćņ”ØĒĢśļŖö Ļ│╝ņĀĢ ņŚåņØ┤ ļĪż ļ¬©ļŹĖļ¦üņŚÉ ļīĆĒĢ£ ņä▒ņ░░ņØś ņłśņżĆņØä ļČäņäØĒĢśņśĆļŗż. ļö░ļØ╝ņä£ ņä▒ņ░░ņŚŁļ¤ēņØś ņ░©ņØ┤Ļ░Ć ņä▒ņ░░ņłśņżĆņŚÉ ņśüĒ¢źņØä ņŻ╝ņŚłņØä ņłś ņ׳ļŗż. ĒĢśņ¦Ćļ¦ī ļČĆņĀĢņĀü ļĪż ļ¬©ļŹĖļ¦üņŚÉņä£ ļ╣äĒīÉņĀü ņä▒ņ░░ņØś ļ╣äņ£©ņØ┤ ļåÆļŗżļŖö ļŹ░ ņØśņØśĻ░Ć ņ׳ņ£╝ļ®░, ĻĖŹņĀĢņĀü ļĪż ļ¬©ļŹĖļ¦üņŚÉņä£ļÅä ļŗ©ņł£ ņä▒ņ░░ņłśņżĆ ņØ┤ņāüņ£╝ļĪ£ ļĪż ļ¬©ļŹĖļ¦üņØä ņä▒ņ░░ĒĢśļÅäļĪØ ĒĢÖņāØļōżņØä ļīĆņāüņ£╝ļĪ£ ņä▒ņ░░ĒĢśļŖö ļ░®ļ▓ĢĻ│╝ ņØśļ»ĖņŚÉ ļīĆĒĢ┤ ĻĄÉņ£ĪĒĢĀ ĒĢäņÜöĻ░Ć ņ׳ļŗż. ļ¦łņ¦Ćļ¦ēņ£╝ļĪ£, ņØ╝Ļ░£ ņØśĻ│╝ļīĆĒĢÖņŚÉ ļīĆĒĢ£ Ļ▓░Ļ│╝ļŖö ļ¬©ļōĀ ņØśĻ│╝ļīĆĒĢÖņŚÉ ļīĆĒĢ£ Ļ▓░Ļ│╝ļĪ£ ņØ╝ļ░śĒÖöĒĢĀ ņłś ņŚåļŗż. ļīĆĒĢÖļ¦łļŗż ĻĄÉņ£ĪĻ│╝ņĀĢņØ┤ ļŗżļź┤Ļ│Ā, ņĪ░ņ¦üļ¼ĖĒÖöņÖĆ ĻĄ¼ņä▒ņøÉņØś ĒŖ╣ņä▒ņØ┤ ļŗżļź╝ ņłś ņ׳ĻĖ░ ļĢīļ¼ĖņØ┤ļŗż.
Ļ▓░ļĪĀņĀüņ£╝ļĪ£, ņØśļīĆņāØņØś ņ×äņāüņŗżņŖĄ ņżæ ņ×äņāüĻĄÉņ£Īņ×ÉņŚÉ ļīĆĒĢ£ ļĪż ļ¬©ļŹĖļ¦üņØĆ ņ×äņāüņĀü Ēā£ļÅäņÖĆ Ļ░Ćļź┤ņ╣śļŖö ĻĖ░ņłĀ, Ļ░£ņØĖņĀü ņ×Éņ¦łĻ│╝ ļČĆņĀĢņĀüņØĖ ļĪż ļ¬©ļŹĖņŚÉņä£ ļéśĒāĆļéśļ®░, ļĪż ļ¬©ļŹĖļ¦üņØĆ ļĪż ļ¬©ļŹĖņØ┤ ņØĖņ¦ĆĒĢśņ¦Ć ļ¬╗ĒĢśļŖö ņāüĒÖ®ņŚÉņä£ ļ░£ņāØĒĢśļ®░, ņØ┤ļŖö ņØśļīĆņāØļōżņØś ņĀäļ¼Ėņ¦ü ņĀĢņ▓┤ņä▒ ĒśĢņä▒ņŚÉ ĻĖŹņĀĢņĀüņØ┤Ļ▒░ļéś ļČĆņĀĢņĀüņØĖ ņśüĒ¢źņØä ļ»Ėņ╣£ļŗż. ļö░ļØ╝ņä£ ņ×äņāü ĻĄÉņ£Īņ×ÉļōżņØś ļĪż ļ¬©ļŹĖļ¦ü ņŚŁļ¤ēņØä Ē¢źņāüņŗ£Ēé¼ ņłś ņ׳ļŖö ĻĄÉņ£ĪĒöäļĪ£ĻĘĖļשņØ┤ ņĀ£ņĢłļÉśņ¢┤ņĢ╝ ĒĢśļ®░, ĒĢÖņāØļōżņŚÉĻ▓īļÅä ņ×ÉņŗĀņØ┤ Ļ▓ĮĒŚśĒĢ£ ļĪż ļ¬©ļŹĖĻ│╝ ļĪż ļ¬©ļŹĖļ¦ü ņāüĒÖ®ņØä ņ×ÉņĢä ņä▒ņ░░ĒĢĀ ņłś ņ׳ļŖö ņä▒ņ░░ĒĢÖņŖĄņØä ņ┤ēņ¦äņŗ£ņ╝£ņĢ╝ ĒĢ£ļŗż.
Acknowledgments
ņŚ░ĻĄ¼ņŚÉ ņ░ĖņŚ¼ĒĢ┤ņŻ╝ņŗĀ ņŚ░ņäĖļīĆĒĢÖĻĄÉ ņøÉņŻ╝ņØśĻ│╝ļīĆĒĢÖ ņØśĒĢÖĻ│╝ ĒĢÖņāØļōżņŚÉĻ▓ī Ļ░Éņé¼ļō£ļ”░ļŗż.
REFERENCES
1. Ficklin FL, Browne VL, Powell RC, Carter JE. Faculty and house staff members as role models. J Med Educ. 1988;63(5):392-396.


2. Wright S, Wong A, Newill C. The impact of role models on medical students. J Gen Intern Med. 1997;12(1):53-56.



3. Mann KV. In: Steinert Y, editor. Faculty development in the health professions: a focus on research and practice. Springer Netherlands; Dordrecht: 2014. p. 245-264. Faculty development to promote role-modeling and reflective practice.
4. Passi V, Johnson N. The impact of positive doctor role modeling. Med Teach. 2016;38(11):1139-1145.


5. Cruess SR, Cruess RL, Steinert Y. Role modelling: making the most of a powerful teaching strategy. BMJ. 2008;336(7646):718-721.



6. Burgess A, Oates K, Goulston K. Role modelling in medical education: the importance of teaching skills. Clin Teach. 2016;13(2):134-137.


7. Adkoli BV, Al-Umran KU, Al-Sheikh M, Deepak KK, Al-Rubaish AM. Medical studentsŌĆÖ perception of professionalism: a qualitative study from Saudi Arabia. Med Teach. 2011;33(10):840-845.


8. Mohammadi E, Mortaz Hejri S, Sohrabpour AA, Mirzazadeh A, Shahsavari H. Exploring clinical educatorsŌĆÖ perceptions of role modeling after participating in a role modeling educational program. Med Teach. 2021;43(4):397-403.


9. Passi V, Johnson S, Peile E, Wright S, Hafferty F, Johnson N. Doctor role modelling in medical education: BEME guide no. 27. Med Teach. 2013;35(9):e1422-1436.


11. Elzubeir MA, Rizk DE. Identifying characteristics that students, interns and residents look for in their role models. Med Educ. 2001;35(3):272-277.


12. Yazigi A, Nasr M, Sleilaty G, Nemr E. Clinical teachers as role models: perceptions of interns and residents in a Lebanese medical school. Med Educ. 2006;40(7):645-661.


13. Wyber R, Egan T. For better or worse: role models for New Zealand house officers. N Z Med J. 2007;120(1253):U2518.

14. Lombarts KM, Heineman MJ, Arah OA. Good clinical teachers likely to be specialist role models: results from a multicenter cross-sectional survey. PLoS One. 2010;5(12):e15202



15. Joubert PM, Kruger C, Bergh AM, Pickworth GE, Van Staden CW, Roos JL, et al. Medical students on the value of role models for developing ŌĆśsoft skillsŌĆÖ: ŌĆ£thatŌĆÖs the way you do itŌĆØ. Afr J Psychiatry. 2006;9(1):28-32.

16. Weissmann PF, Branch WT, Gracey CF, Haidet P, Frankel RM. Role modeling humanistic behavior: learning bedside manner from the experts. Acad Med. 2006;81(7):661-667.


17. Wright SM, Carrese JA. Which values do attending physicians try to pass on to house officers? Med Educ. 2001;35(10):941-945.


18. Murakami M, Kawabata H, Maezawa M. The perception of the hidden curriculum on medical education: an exploratory study. Asia Pac Fam Med. 2009;8(1):9



19. Wear D, Aultman JM, Zarconi J, Varley JD. Derogatory and cynical humour directed towards patients: views of residents and attending doctors. Med Educ. 2009;43(1):34-41.


20. Han H, Suh B. Current Status and directions of professional identity formation in medical education. Korean Med Educ Rev. 2021;23(2):80-89.

21. Benbassat J. Role modeling in medical education: the importance of a reflective imitation. Acad Med. 2014;89(4):550-554.


22. Holden MD, Buck E, Luk J, Ambriz F, Boisaubin EV, Clark MA, et al. Professional identity formation: creating a longitudinal framework through TIME (Transformation in Medical Education). Acad Med. 2015;90(6):761-767.

23. Abrams MP, Eckert T, Topping D, Daly KD. Reflective writing on the cadaveric dissection experience: an effective tool to assess the impact of dissection on learning of anatomy, humanism, empathy, well-being, and professional identity formation in medical students. Anat Sci Educ. 2021;14(5):658-665.


24. Cunningham H, Taylor D, Desai UA, Quiah SC, Kaplan B, Fei L, et al. Looking back to move forward: first-year medical studentsŌĆÖ meta-reflections on their narrative portfolio writings. Acad Med. 2018;93(6):888-894.



25. Wald HS, White J, Reis SP, Esquibel AY, Anthony D. Grappling with complexity: medical studentsŌĆÖ reflective writings about challenging patient encounters as a window into professional identity formation. Med Teach. 2019;41(2):152-160.


26. Wald HS, Borkan JM, Taylor JS, Anthony D, Reis SP. Fostering and evaluating reflective capacity in medical education: developing the REFLECT rubric for assessing reflective writing. Acad Med. 2012;87(1):41-50.


27. Stern DT, Papadakis M. The developing physician: becoming a professional. N Engl J Med. 2006;355(17):1794-1799.


28. Mohammadi E, Mirzazadeh A, Shahsavari H, Sohrabpour AA. Clinical teachersŌĆÖ perceptions of role modeling: a qualitative study. BMC Med Educ. 2021;21(1):261



29. Bahmanbijari B, Beigzadeh A, Etminan A, Najarkolai AR, Khodaei M, Askari SM. The perspective of medical students regarding the roles and characteristics of a clinical role model. Electron Physician. 2017;9(4):4124-4130.



30. Armyanti I, Mustika R, Soemantri D. Dealing with negative role modelling in shaping professional physician: an exploratory study. J Pak Med Assoc. 2020;70(9):1527-1532.


31. Burgess A, Goulston K, Oates K. Role modelling of clinical tutors: a focus group study among medical students. BMC Med Educ. 2015;15:17



32. Keis O, Schneider A, Heindl F, Huber-Lang M, Ochsner W, Grab-Kroll C. How do German medical students perceive role models during clinical placements (ŌĆ£FamulaturŌĆØ)?: an empirical study. BMC Med Educ. 2019;19(1):184



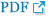
-
METRICS

-
- 1 Crossref
- 0 Scopus
- 651 View
- 13 Download
- Related articles







 PDF Links
PDF Links PubReader
PubReader ePub Link
ePub Link Full text via DOI
Full text via DOI Download Citation
Download Citation Print
Print